Equine
Equine Sand Colic – A Dirty Situation
By Garrett Metcalf, DVM
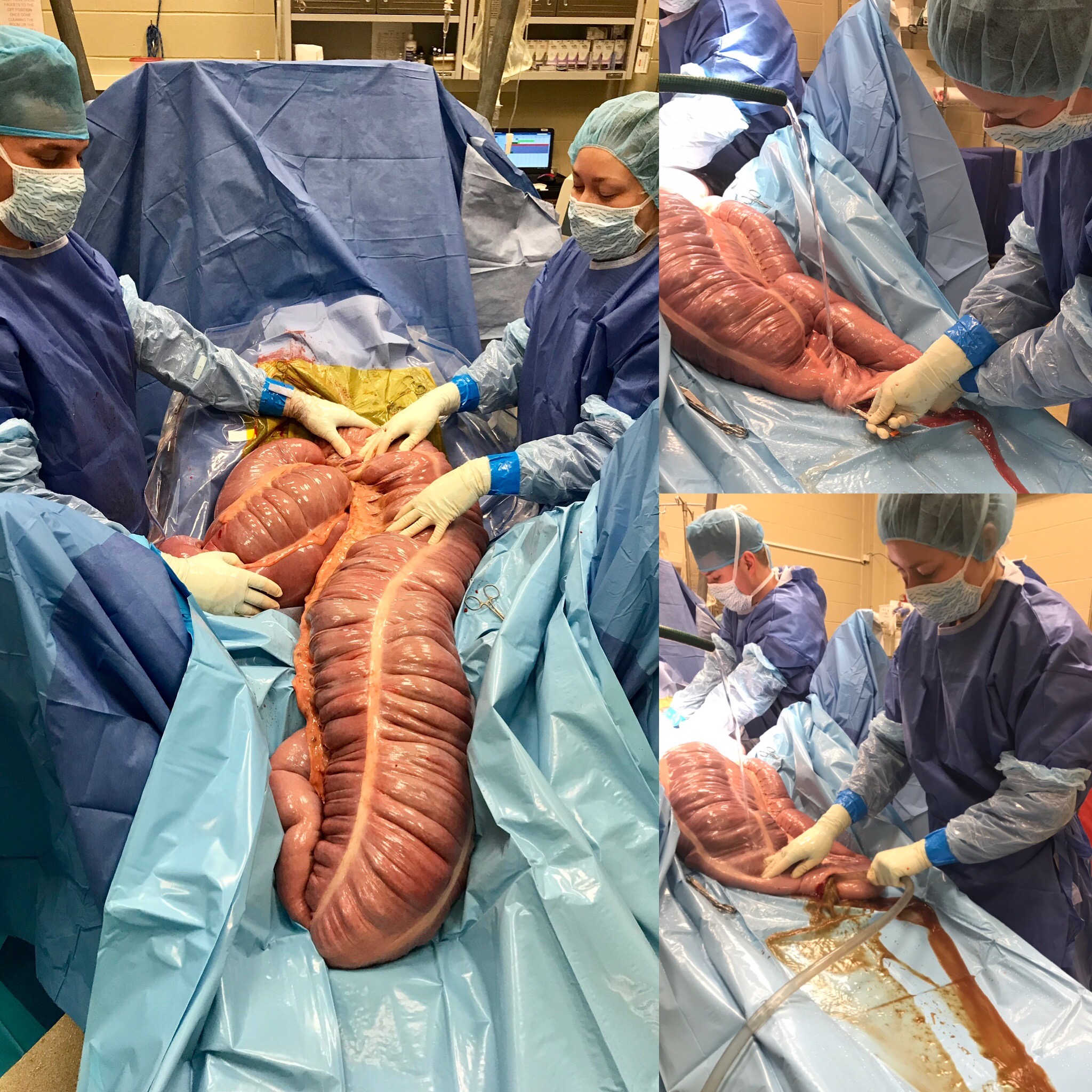
Many people find the sounds of waves moving across sandy beaches on a nice comfortable vacation enjoyable, but hearing them with a stethoscope on a horse’s abdomen is no vacation and certainly not comfortable for the horse. Sand colic is one of many forms of colic that owners should be aware of because it can be very preventable that every horse owner can address easily at the farm.
Sand colic is an accumulation of sand, dirt or gravel that the horse ingests over a short or long period of time. The sand accumulates typically in the large colon of the horse where it can lead to colonic irritation (colitis), abnormal colon motility and obstruction similar to an impaction. All age groups of horses are susceptible to sand colic, but younger horses are more likely to preferentially ingest sand or dirt. Sandy loose soil or small gravel landscape that the horses are housed in can predispose horses to sand colic especially if the horses are fed on the ground or if the horses are prone to dropping feed on the ground and then they proceed to eat the feed from the ground.
Clinical Signs
A horse suffering from sand colic cannot be differentiated from other forms of colic without a clear history from the owner or without performing diagnostic tests. Horses can display a large range of clinical signs from horse to horse depending on the severity of sand accumulated in the colon or if there are secondary complications associated with the sand colic. Common clinical signs can be lethargy, inappetence and loose manure or diarrhea. Of course when the horse becomes painful, classic signs of colic are seen such as rolling, pawing, getting up and down frequently, flank watching or stretching out. Again these signs can overlap with many causes of colic so further work up is needed to determine the cause of the colic symptoms.
Diagnosis
Sand colic typically can be diagnosed multiple different ways. Auscultation of the very lowest point of the abdomen over the large colon can produce a distinct sound that sounds similar to ocean waves or water rushing over sand. Ultrasound can help make the diagnosis, but it can be difficult to differentiate the type of material present in the colon. Suspending the manure with water in a clear plastic bag or rectal sleeve will allow separation of the sand from the manure to help increase the suspicion of sand colic. Rectal exam can also lead to suspicion or diagnosis of sand colon. A definitive diagnosis of sand colic is made by taking an x-ray or radiograph of the abdomen. Sand or gravel will be detected on an x-ray and also can be used to measure the severity or amount of sand accumulation in the colon. A radiograph can also be used to monitor progress of treatment allowing quantification of the amount of sand being removed from the colon over time, which is rather helpful to determine progress of the treatment.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the sand colic, amount of sand in the colon or the systemic health of the horse there are a few treatment options. If the horse’s pain level cannot be controlled, improvement with other treatments fail or the horse is systemically compromised, surgery is indicated to removed the sand impaction and correct other abnormalities that may occur secondarily to the sand impaction. If the horse’s pain can be controlled and is able to maintain normal motility or passage of ingesta through the colon, medical treatment can be successful at treating sand impactions. Medical treatment typically requires IV fluids, pro-motility drugs and administration of mineral oil with psyllium (Metamucil) to help clear the sand from the colon. Research studies have indicated that the combination of mineral oil and psyllium had the fastest resolution of sand from the colon when monitored with radiographic measurements of sand in the colon.
Prevention
Basic steps can be taken to reduce the risk of horses developing sand colic at home. First step is to monitor the horse’s behavior to assess if they are horses that are messy eaters and like to scrounge for scraps of food off the ground. Evaluate the housing situation the horse is in and the soil type that is present on the farm. Keep horses from dropping feed on the ground by feeding in raised feed bunks or feeding on rubber mats can help mitigate the amount of sand or dirt ingested. In horses where environment cannot be easily controlled, feeding intermittent psyllium products such as sand clear will help removed accumulated sand in the large colon before it causes sand colic. Recommendation is to feed psyllium one week out of every mouth to help reduced the risk of sand colic.
While it is rather difficult to control everything in your horses’ daily lives or control every environmental factor, steps can be taken to help reduce the risk of this particular cause of colic. Recognizing signs of colic quickly and seeking veterinary care is always a good idea no matter the cause of the colic symptoms.
Equine
Equine Flexural Limb Deformities
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf
Flexural limb issues can occur in different age groups of horses, starting with newborns up to two- to three-year-olds. These issues occur somewhat predictably in age groups and can be addressed rather quickly when needed. There are various treatments and methods that can be used to address flexural issues. This article will discuss the most common flexural abnormalities and treatment methods.
Foal Flexural Issues
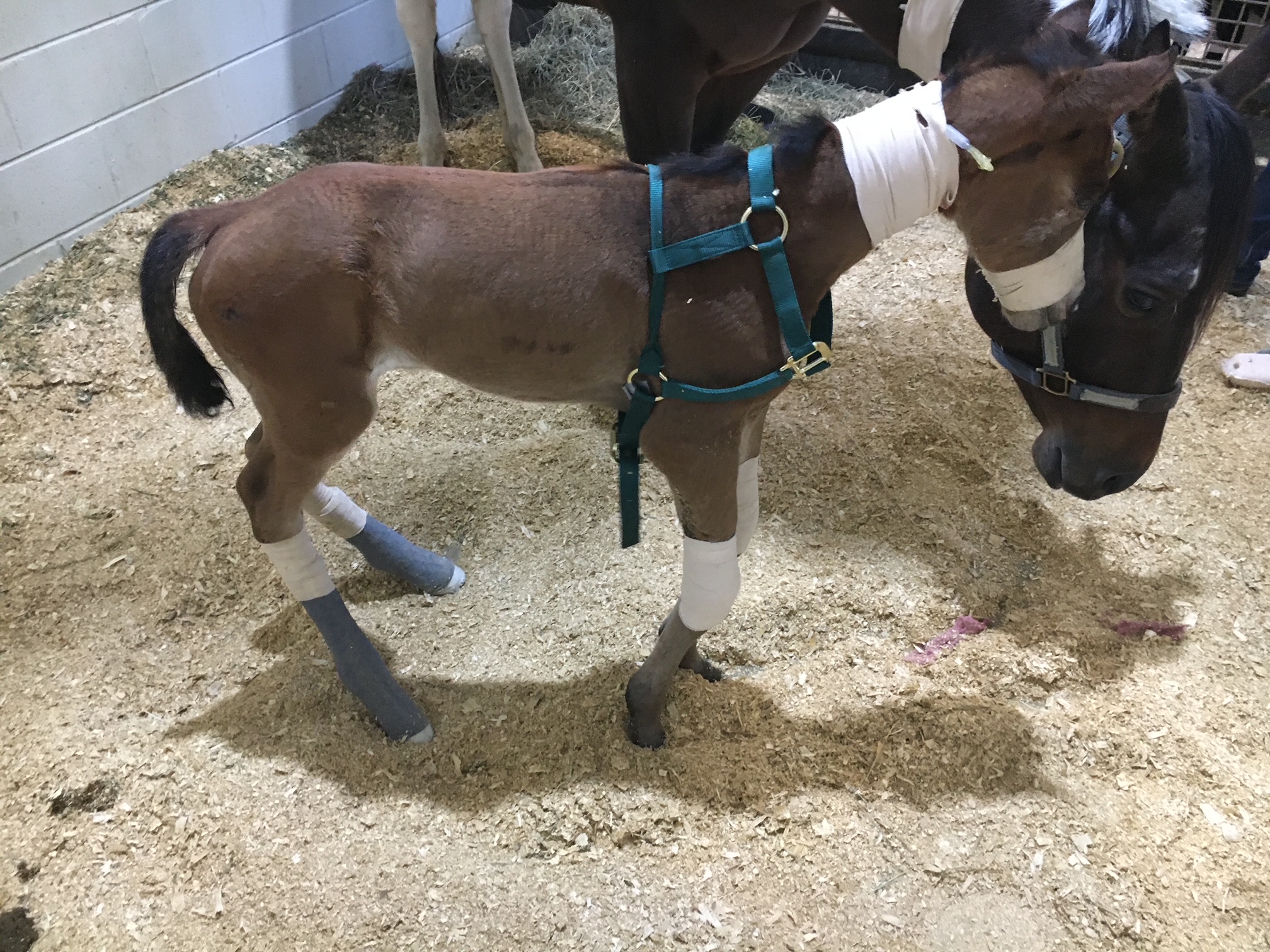
Foal flexural issues are often considered congenital flexural limb abnormalities because they are born with them. We don’t fully understand why this occurs but there is some evidence in the human literature that lack of fetal activity in the womb causes club feet in babies. In foals, it is thought that uterine positioning is to blame for part of the contracted tendons. Other causes can be exposure of the mare to toxic plants or substances that may be toxic to the fetus.
The most common area that a foal will have contracture of limb is at the carpus or knee. These foals will not be able to fully extend the knee and often will affect both at the same time. These foals can have difficulty standing to nurse or will get fatigued quickly and will not be able to stand for longer periods of time. There can also be damage to the extensor tendons or even rupture of extensor tendons caused by the high strain placed on them when the foal tries to stay standing. The rupturing of these tendons is not overly concerning but the lack of extensor function can make the flexural limb deformity worsen.
Other common locations of flexural limb deformities can be at the fetlock or coffin joint level. These deformities are not usually as detrimental to allowing the foal to stand and nurse properly compared to carpal flexural deformities. These deformities can be addressed similar to carpal deformities with some exceptions.
Treatment of Flexural Deformities
Splints or casts can be used to stretch and support the effected limbs of foals. Splints are often preferred by most veterinarians because they can be repositioned or reset as needed. Splints are easier to place on the limbs of foals but they do need resetting every 24 to 48 hours. Casting of the limbs is more rigid but is not adjustable once placed. Casting is often needed in more severe cases and requires changing frequently. Whenever placing these devices, care must be taken to prevent splint or cast sores because foal skin is rather delicate.
Surgical intervention is needed in some cases of carpal flexural deformities. A study out of Australia found that cutting of two muscle/tendon groups on the back of the carpus greatly improved the ability to extend the carpus with splinting methods. Cutting of these tendons do not have consequence to future athletic function. The two muscles are called flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnaris lateralis.
An antibiotic called Oxytetracycline is helpful to treat flexural limb deformities because of its side effect of causing tendon laxity. The laxity is created by chelating calcium within the tendons and allows the relaxation of tendons. This method does have some risk because of the high dose required and renal injury that it can cause when not administered with IV fluids.
Toe extension shoes are used when it comes to dealing with lower limb flexural limb deformities. These shoes are often applied with adhesives and after the splinting or casting is no longer needed. The toe extension shoe allow foal to continue to stretch those tendons every time they take a step and prevent from becoming contracted again.
Older horses (six months or older) with contracted tendons often get acquired limb deformities and the horses need surgical intervention to correct these deformities. These surgeries cut or release check ligaments that allows the musculotendinous unit of the deep digital or superficial digital flexor tendon to elongate. The deep digital flexor tendon is responsible for causing club feet or a flexural limb deformity at the coffin joint. The superficial digital flexor tendon is responsible flexor tendon that causes a flexural limb deformity at the fetlock joint. The check ligaments attach the tendon to bone and do not allow the tendon to elongate past a certain point. By eliminating these ligaments the flexural limb deformity can be corrected by allowing the muscle to stretch since the tendon is much more rigid.
Flexural limb deformities can be caused by excessive laxity or weakness of the tendons. These deformities are often seen in premature foals or foals that are born at a much smaller birth weight. The excessive laxity will cause the toes of there feet to flip up in the air and the fetlocks to be touching the ground. The areas where the skin is contacting the ground will cause sores and abrasions. If these areas are note protected the wounds can get into deep structures causing serious infection and injury the flexor tendons.
Treatment for tendon laxity is to add heel extension shoes to keep the toes flat to the ground. The extension behind the foot forces the toe down under the foals own weight. As the foal becomes stronger from normal activity the muscle attached to the tendons can support the foal and the limb laxity will correct itself. Abrasions still can occur even with heel extension shoes are in place so bandages need to be applied to protect these areas.
Flexural limb issues are a common issue that horses and owners will face. It is best to have your horse evaluated by a veterinarian whenever these problems are suspected. Foal flexural limb deformities can be life threatening because of the limitation of standing on time to nurse colostrum. Without colostrum within the first hours of life the foal is a much higher risk of sepsis and death.
Read more in the August 2023 issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
Equine
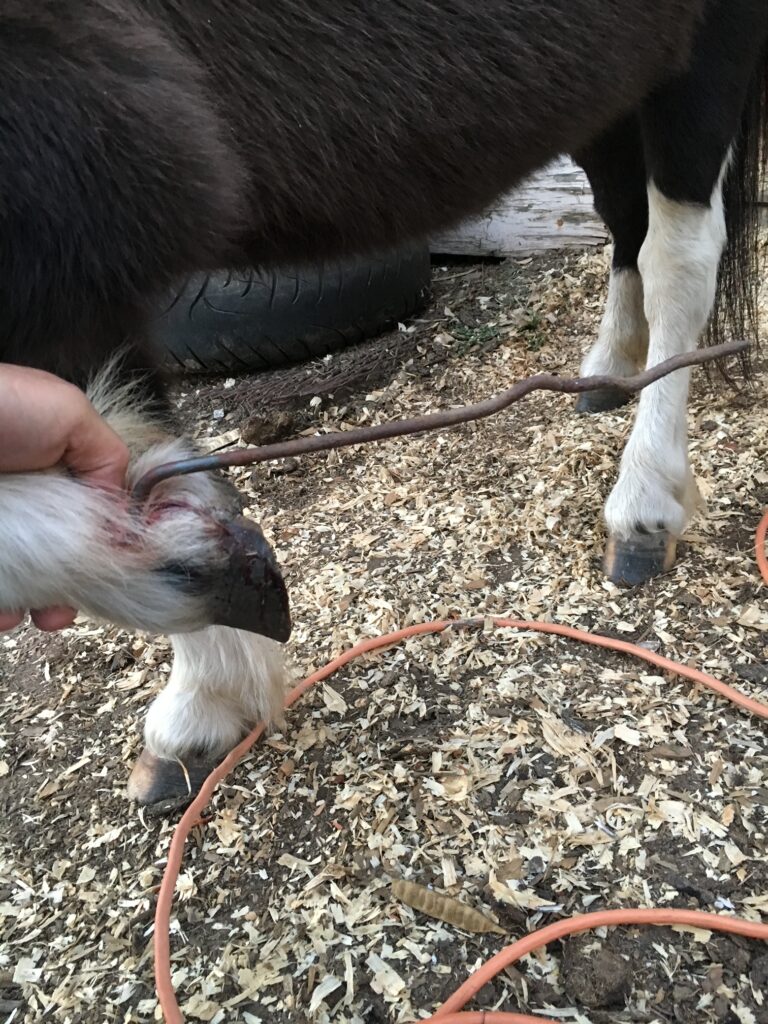
Equine Foot Abcesses
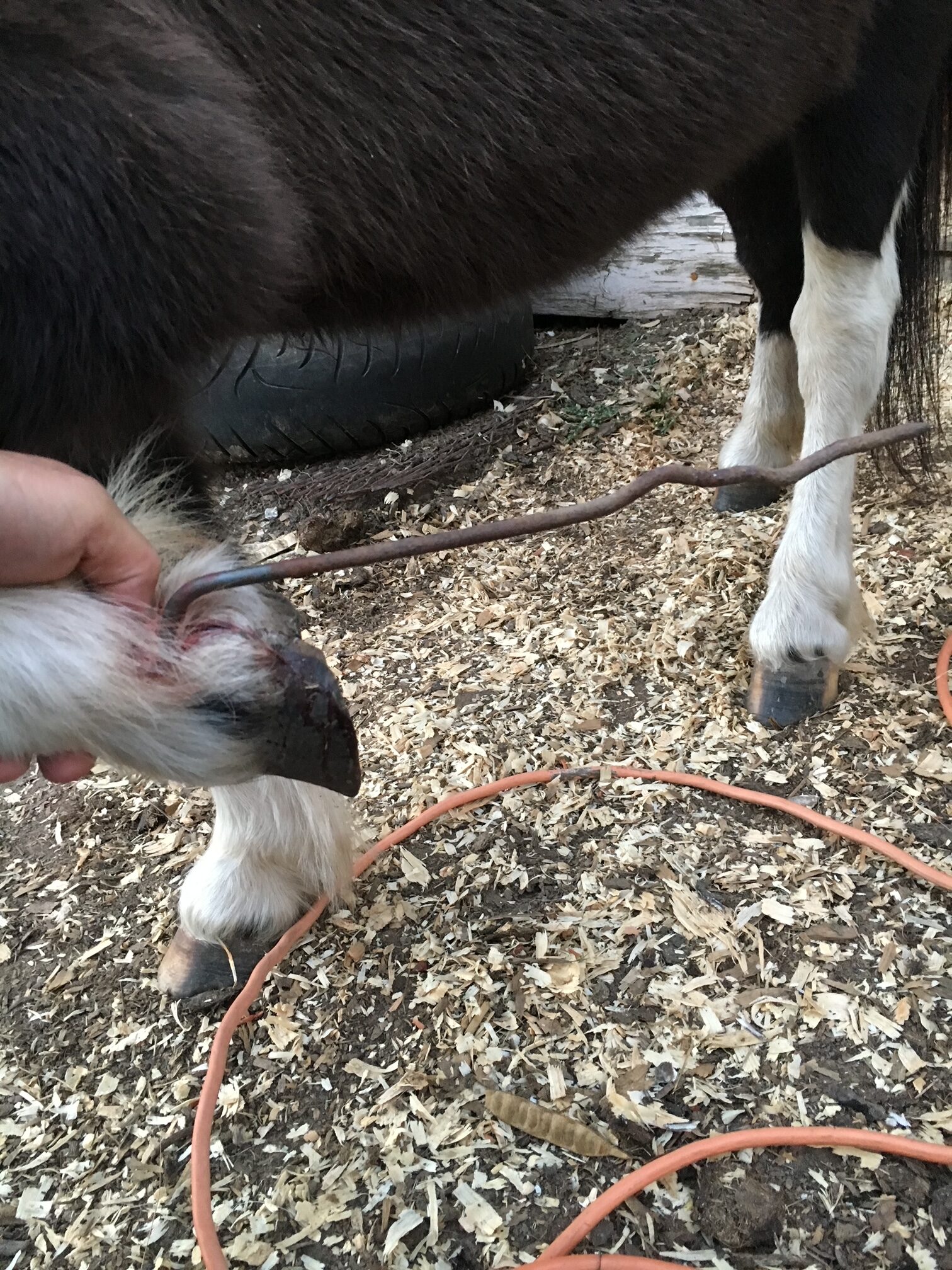

What a pain!
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf, DVM
A foot abscess is a common occurrence in horses throughout the year. Often wet weather can play a factor in the increase number of foot abscesses that horses will experience. A foot abscess can cause a great deal of pain, lameness, swelling and misery to the horse that often needs to be addressed quickly and provide pain management to keep them comfortable. There are many methods of addressing a foot abscess that people use. This article will discuss techniques to evaluate and treat the abscess as quickly as possible.
Foot abscess is a focal or sometimes diffuse infection that is trapped between the sensitive and non-sensitive lamina of the foot capsule. A foot abscess can form randomly from the normal stresses and environmental changes that cause the foot to allow bacteria to enter down to the sensitive tissues. Other causes are penetrating injuries to the bottom of the foot that allows bacteria to enter the through the outer lamina, such as nails, sharp rocks or even thorns. Poor foot care and misplaced shoeing nails can also lead to foot abscesses. A common area for abscesses to form is at the white line (area where the sole and hoof wall meet) and at the bars of the heels.
Foot abscess can cause a horse to have variable amounts of lameness, but generally they will be lame at a walk or even be non-weight bearing from the severity of the pain. Swelling starting at the foot and working its way up the limb can be noted when the abscess is trying to migrate out at the coronary band. These types of abscess are often referred to as “gravel” abscesses. “Gravel” is no more than just a regular foot abscess that has found the path of least resistance to the coronary band, where it ruptures out and causes a draining tract. An abscess in the hind foot can make the horse move rather abnormal to the point that it makes owners and veterinaries perceive the horse as acting neurologic.
Examination of the horse for lameness is the first step in diagnosing a foot abscess. The horse will often be lame at walk but some need to be watched at a trot to determine the lame limb. Lameness localization with regional nerve blocks can help make sure the pain is coming from the foot and not other parts of the limb. The foot will often have an increase digital pulse with occasional notable heat in the foot. The pulse is from inflammation causing a bounding of the digital arteries most notably behind the ankle region. The foot examination often needs to be performed with the shoe removed from the foot if the horse is shod. Hoof testers help pinpoint the area of most concern on the foot and often horses will be rather painful in response to the pressure created by the hoof testers. Knifing the foot out to clean up and remove any old sole or frog material is imperative to be able to locate the abscess with as much accuracy as possible. Often there will be a defect in the hoof or a dark focal tract that will lead to the abscess.
Treatment of the foot abscess can be done multiple ways and many people have lots of opinions on this topic. My treatment of choice is to open that abscess as soon as possible to give the horse nearly immediate relief and to quickly resolve the abscess infection. There are many methods to doing this but a good sharp hoof knife or loop knife one of the easiest ways to get the abscess drainage through the bottom of the foot. Whenever drainage of the abscess is achieved at the bottom this can eliminate the formation of a “gravel” and keep it from migrating out at the coronary band. Also drainage at the bottom allows a more effective treatment of the abscess with topically applied poultice agents. After the abscess has been opened to drain, bandaging the foot with a poultice agent is effective at eliminate the abscess and preventing foreign material from packing to the abscess area.
A great method of bandaging the foot is with the use of a large baby diaper. The diaper is very absorbent and foots the foot rather well. The diaper can be covered with layers of Vetrap, Duck Tape and Elaskiton to keep it protected or the foot can be placed in a medicine boot to keep the diaper protected.
Poultice choices are rather personal experience or availability, but also depend on the nature of the abscess. Epsom salt based foot poultice agent called Magna Paste or similar products are rather good at drawing out the remaining part of the abscess once it is opened. A homemade poultice of sugar combined with Betadine solution can make a really good poultice. There are various other topical agents that can be used effectively. The main thing when choosing a topical product is to make sure it is safe and that it has some antimicrobial properties.
Some foot abscess cases can be difficult to pinpoint and to drain. In these situations often time, pain management and soaking of the foot in Epsom salt water baths can help to allow the abscess rupture or make it easier to identify. In rather difficult abscess or when abscesses keep reoccurring in the same location, X-ray imaging of the foot is helpful to examine the structures of the foot. The abscess itself cannot be seen often with X-ray because the abscess fluid is the same density as the hoof wall. The only way to identify an abscess on X-ray is if there is gas present in the abscess making it visible on the film. Whenever there is a penetrating injury to the foot, X-ray is a must to make sure that the injury is not going into the deeper structures of the foot like the coffin joint or navicular bursa. These injuries are much more serious and need to be examined as quickly as possible. It is also recommended whenever possible to leave the penetrating object in the foot until the X-ray is taken. This will help the veterinarian understand what structures may have been injured.
Prevention of foot abscess is not always possible but a great start to this is really good hoof care. Routine trimming on a timely schedule is key part of good hoof care. The longer the feet go without a trim can affect the lamina and cause stretching of the white line, opening it up to allow bacteria to enter the foot. The use of special shoeing nails and other methods of good shoeing practices also limit the risk of abscessation.
Read more in the June issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
Equine
Guttural Pouch Diseases of Horses
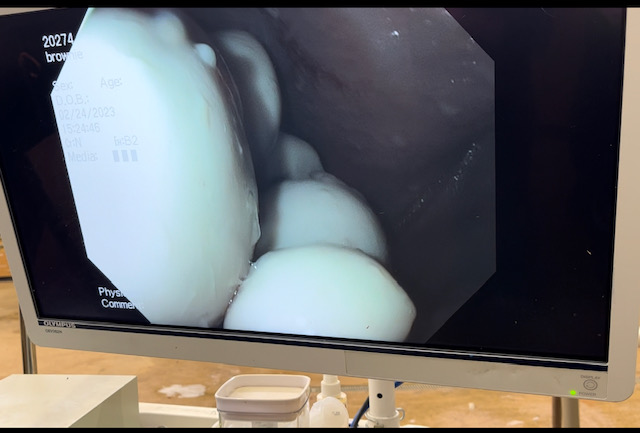
The guttural pouches of horses may not be very well known to most horse owners. These bilaterally paired pouches are located below the base of the skull, below the ears and extend into the throat latch region. The pouches purpose is not fully understood, but some theories is that they reduce the weight of the skull or have a blood cooling function to reduce the temperature of the arterial blood going to the brain. The guttural pouches can be plagued with a multitude of issues that are difficult to treat or can be life threatening to the horse. Other species contain guttural pouches such as some bats, American Forest mouse and Hyraxe.
The anatomy of the guttural pouches is complex and houses various important anatomic structures. The guttural pouches are an auditory tube diverticulum that is analogous to human Eustachian tubes but much larger. The volume of the guttural pouches can be up to 400-600 milliliters of air. The guttural pouches contain large arteries, nerves, the bones of the inner ear, muscle tissue and part of the hyoid apparatus that connects the skull to the larynx. The opening of the guttural pouches is deep in the nasopharynx through the slights call the pharyngeal ostium, which can only be accessed with an endoscope passed up the nose. The difficulty of accessing this area makes treatment of these diseases challenging at best. The guttural pouch is the only location in the horse that allows direct visualization of the arteries and nerves. The main arteries that are present in the guttural pouch are the maxillary artery and the internal and external carotid arteries that provide all the blood to the skull. The nerves in the guttural pouch are cranial nerves that exit directly from the brain or brain stem that innervate critical structures that control breathing, swallowing, chewing and ocular functions of the skull.
Read more in the April issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
-

 Country Lifestyle7 years ago
Country Lifestyle7 years agoJuly 2017 Profile: J.W. Hart
-

 Outdoors6 years ago
Outdoors6 years agoGrazing Oklahoma: Honey Locust
-

 Country Lifestyle2 years ago
Country Lifestyle2 years agoThe Two Sides of Colten Jesse
-

 Attractions7 years ago
Attractions7 years ago48 Hours in Atoka Remembered
-

 Farm & Ranch5 years ago
Farm & Ranch5 years agoHackberry (Celtis spp.)
-

 Outdoors4 years ago
Outdoors4 years agoPecan Production Information: Online Resources for Growers
-

 Equine7 years ago
Equine7 years agoUmbilical Hernia
-

 Country Lifestyle1 year ago
Country Lifestyle1 year agoSay Yes!





