Equine
Raising the Bar – Cody Hollingsworth
When Oklahoma State University Alumnus Cody Hollingsworth was first approached to take the reins of the college’s rodeo team, the partnership was obviously a perfect fit.
The Colorado cowboy had attended Oklahoma State and competed as a bull rider on the rodeo team in the mid-1990s before transferring back to his home state, where he earned his Bachelor of Science degree in agricultural business and animal science.
The pull from Stillwater was strong, so in 2009, Hollingsworth, his wife Katie, and daughter Lyndsey packed their bags and moved south, settling in just miles from the campus. The Hollingsworths owned a marketing agency called Western Integrity Agency, which specialized in the equine and rodeo industry.
Shortly after the move, they were approached for a sponsorship by then OSU student and Rodeo Team member Courtney DeHoff. “Of course, with my ties to OSU rodeo, it was almost an immediate ‘yes’ when we saw what it was for. So, we agreed to sponsor, but said they had to let us help with the sponsor packets through our marketing company,” he recalled. “We just volunteered to dive in to help with the sponsorships and other stuff. That started the relationship with the team.”
Barely a year later, several rodeo team donors and supporters, requested a meeting to discuss officially running the program. “It all just fell into place after that,” he said.
Day to Day
With the title of Rodeo Program Coordinator and Head Coach, Hollingsworth wears many hats throughout the day. Typically, each morning begins with office hours, during which time he handles program duties ranging from recruiting to fundraising to managing the facility.
He also works directly with students to ensure their academics are in order. “I also work with the Student Success Center in the Ferguson College of Agriculture doing academic advising,” he explained. “As proud as we are of the students who compete on the rodeo team for the success they have in the arena, it’s even more important that they find that success in a career when they graduate.”
Shortly after lunch, he moves to the rodeo facility, located northwest of town. He and his two graduate students, Lariat Larner and Zane Grigsby, begin the regularly scheduled practice at 3 p.m.
The practices are scheduled Monday through Thursday, with every team member honing their skills. Practices for the various events are typically staggered throughout the afternoon, ensuring each member gets the time and coaching they need. “I try to be everywhere and help out as much as I can for each event, and luckily I have Lariat and Zane assisting with managing, organizing, and running practice,” Hollingsworth explained.
The OSU Rodeo Team facilities makes practicing multiple events at one time relatively painless. The large outdoor arena is typically used for barrel racing and team roping, and an additional calf lane is utilized by the calf and breakaway ropers. There is also a smaller covered arena that houses the bucking chutes, although it is large enough to accommodate the other events in the case of implement weather.
Although a bull rider himself, Hollingsworth has developed a knowledge of all the events. “It’s definitely been a challenge to learn as much about each event as possible so that I can be helpful to all the members of the team,” he admitted.
There is one speed event that he’s become even more well-versed at over the years – barrel racing. Both Katie and Lyndsey run barrels, and the family has raised and trained several of their own futurity and rodeo horses. “I have some techniques and knowledge in a few areas you might not expect,” he said with a laugh.
Challenges & Accomplishments
While a dream job, Hollingsworth knew there would be challenges along the way. The first being the restructuring of how the program was ran. “It was entirely a student-run organization before I came on. They had a volunteer faculty advisor, and it was less organized. The students were used to just doing their own thing, and so that first year definitely demanded some work to get things organized and running smoothly so that the students could continue to improve,” he shared.
The other obstacle? Funding.
“I would get comments like, ‘Why doesn’t the school just fund this or fund that?’ It’s just like anything else in that trying to create funding where there was no line item in the past for that was very difficult. Everyone does all they can to balance their budgets and make things work well, and then when something is added in that hasn’t been funded before, it can be tough,” Hollingsworth explained.
He gives a large amount of credit for the Rodeo Team’s current financial situation to Cynda Clary, the Associate Dean of the Ferguson College of Agriculture, who was hired shortly after Cody. “She has given us a great bit of help and has tried to add that funding and find extra in the budget. Honestly, I don’t know how long this position would have lasted if it wasn’t for her and her work there,” he said.
Now, the Rodeo Team is able to provide scholarships to worthy students, maintaining and developing the facility, as well as travel support for the students. Over the years Hollingsworth and the team has grown the fundraising efforts, which are highlighted by the Cowboy Ball held each February. “We are always looking for ways to expand scholarships and build on our facilities,” he said. “Donor opportunities are currently available. If someone is interested in donating, they can contact me directly or visit with Dusty Bedwell at the OSU Foundation.”
Finally, the incredible growth of the program has been a double-edged sword, causing logistical difficulties in practice and travel. When the National Intercollegiate Rodeo Association announced, as did the NCAA, that college seniors would have another year of eligibility, the number of team members increased even more.
“When I first started, there were maybe 20 students in the organization, and I never took more than a dozen students to the rodeos,” Hollingsworth remembered.
This year the program boasts 54 students, with nearly 50 traveling to the first two rodeos of the season. “Everyone is a little bigger and busier than normal, but that’s why it was important to develop the graduate assistant positions. We had one already, but we grew so much we were able to add a second one,” he said.
Those challenges are worth it, as the OSU Rodeo Team has become a regular contender at all levels of collegiate competition. In 2019, the women’s team won the Central Plains Regional Championship, punching their ticket to the Collegiate National Finals Rodeo. Each year, the Cowboys can boast of taking several students to the CNFR. “It is extremely gratifying to see the program grow so much. Embracing that growth and raising the bar in competition as high as the team has is very rewarding,” Hollingsworth said. “When I got here, the students didn’t have a lot of support. You’d have a few decent students every now and again, but now we are at the point where we always have competitive students, and we’re able to build on that consistency.”
Although Hollingsworth can be found across the country attending the major youth rodeo events such as the National High School Finals Rodeo and the International Finals Youth Rodeo to recruit members, the success of the team now regularly draws talented individuals to Stillwater.
While talent in the arena is an important component of a prospective student’s resume, their performance in the classroom and drive for career success carries just as much weight. “The main thing a high school or junior high student – one that wants to compete on the rodeo team – needs to focus on is academics. We want to ensure we recruit students who are going to be successful,” Hollingsworth said. “They are student athletes, but they know they can come to a Division One school, get a quality education, and still get to be on a competitive team.”
He added that once those students begin to progress through high school, they can send in videos of their competition runs and their accomplishments. “We will look at those, and that will ensure they’re on our list of students to watch and be aware of,” he said.
Equine
Fly Control That Works: What’s Worth Your Money This Summer

By Ann Asher
Every year about this time, it feels like the flies start winning. No matter how clean I keep the pens or how many fly strips I hang, they show up in clouds. Over the past few summers, I’ve tried just about everything—feed-through supplements, predator bugs, DIY traps, and plenty of fly sprays. Some things helped. Some were a waste of money. If you’re battling flies this year, here’s what’s actually worked for me—and what research says can make a real difference on the farm or ranch.
Start with Cleanliness (But Know It’s Not Enough)
The first—and most repeated—advice is to stay ahead of the mess. Manure management is critical, especially around barns, pens, and loafing sheds. Flies lay eggs in fresh manure, and those eggs hatch into larvae in as little as 24 hours during warm weather.
I try to clean high-traffic areas at least every other day, but the truth is, even on the cleanest farms, flies can still be a problem because of moisture, standing water, and nearby neighbors.
Feed-Through Fly Control: A Solid Foundation
One thing that made a noticeable difference for my horses and cattle was starting a feed-through larvicide early in the season. These products add a growth regulator to the feed that passes through the animal and prevents fly larvae from developing in manure.
It’s not an instant fix—you won’t see fewer flies for several weeks—but once it kicks in, you’ll notice fewer new flies being born.
Tip: Feed-through products only work if all animals on the property are eating it consistently. Otherwise, you’re just treating part of the manure, and flies will keep breeding.
Fly Predators: Small, Mighty, and Surprisingly Effective
Last year, I tried fly predators for the first time. These are tiny, non-stinging insects that lay their eggs in fly pupae, stopping the next generation.
I was skeptical (and honestly a little creeped out at first), but I noticed that where I used predators around the barn and dry lots, the fly pressure dropped. Some companies even offer subscription services that send predators timed to your local climate.
Tip: Fly predators don’t kill adult flies—they stop future flies. So you still need to control the adults already buzzing around.
Good Old-Fashioned Fly Traps
In areas like the barn aisle and outdoor runs, nothing beats physical traps.
I like a combination approach:
- Sticky ribbons and strips for indoor areas
- Odor-baited traps placed away from livestock areas to draw flies away
Tip: Hang baited traps a good distance from barns or stalls. Otherwise, you’re luring flies right into your animals’ space.
Fly Sprays: Choose Carefully
Fly sprays are the first thing most of us reach for—and they do help—but they have limits.
For horses, sprays containing pyrethrins, pyrethroids (like permethrin), or natural oils tend to offer the best repellency. Even then, most sprays only last a few hours, especially if animals are sweating heavily.
Tip: Apply before morning turnout and again before evening if possible. Reapplication is important, especially after heavy exercise or rain.
Other Tools That Help
- Fly masks and fly sheets — particularly those with UV protection, to protect sensitive areas like the eyes and ears
- Fans in barns and run-in sheds — flies struggle to land in strong airflow
- Automatic sprayer systems — an investment, but highly effective for larger barns
The bad news? There’s no magic bullet for fly control.
The good news? Combining several methods—manure management, feed-through treatments, predators, traps, and targeted sprays—can actually make summer bearable for you and your livestock.
At the end of the day, I figure if I can cut the fly population by half, I’ve already made life better for my animals—and a lot less miserable for myself.
References:
- Texas A&M AgriLife Extension – Managing Flies on Livestock
- University of Kentucky Entomology – Controlling Flies Around Livestock
- North Carolina State Extension – Livestock Pest Management
- USDA Agricultural Research Service – Fly Management Resources
- Spalding Labs (for info on biological control programs) – Fly Predators Information
Equine
Horse Pasture ManagementBy OKFR Staff

As spring weather arrives, horse owners are often eager to turn their horses out to graze and exercise—but is the pasture truly ready?
With proper management, pastures can serve as a high-quality forage source and a safe space for exercise. Effective management can even extend the forage production season, helping to reduce hay expenses. On the other hand, unmanaged pastures often develop weed problems, lack nutritional value, and can pose health risks for horses.
Here are five key steps to help improve and maintain horse pastures:
1. Soil Testing, Fertilizing, and Liming
Annual soil testing is ideal, but due to cost, testing every five years for grazing pastures and every three years for hay fields is a reasonable alternative. Grazing pastures tend to lose nutrients more slowly than hay fields because some nutrients are returned to the soil through horse waste, whereas nutrients in harvested hay are removed entirely.
For guidance on soil testing, fertilization, and liming, producers can refer to the Oklahoma Forage and Pasture Fertility Guide, available through Oklahoma Cooperative Extension and OSU’s Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources.
2. Over-Seeding and Renovating Bare Spots
Over-seeding helps replenish forage stands and prevent weed invasion. Use a high-quality pasture seed mix, limiting legume content to no more than 25 percent to avoid excessive salivation in horses.
3. Sacrifice Area
Creating a sacrifice area—a small, fenced section (approximately 300 square feet per horse)—gives overgrazed pastures time to recover during periods of heavy grazing or adverse weather. Horses kept in sacrifice areas should always have access to clean water, adequate hay, good drainage, and waste management.
4. Rotational Grazing
Horses are more selective grazers than cattle and will often overgraze their preferred plants, eventually killing them. This leads to spot grazing and pasture degradation. Rotational grazing allows plants time to regrow and helps reduce waste due to trampling.
Manure concentration in preferred areas also decreases grazing efficiency and nutrient distribution, making rotation an essential tool. Horses should be moved to a new pasture when forage is grazed down to 3–4 inches in height.
5. Weed Control
Chemical herbicides are commonly used to manage weeds, but identifying the specific weeds present is essential for selecting the right treatment. To prevent herbicide resistance, avoid long-term use of the same active ingredient and consider complementary methods such as mowing.
Maintaining healthy pasture also includes proper fertilization and rotational grazing, which both help minimize weed invasion.
Forage Selection and Toxic Plant Awareness
Selecting the right forage species depends on factors like land resources, management goals, and available capital. A mix of cool- and warm-season forages generally provides the most cost-effective year-round grazing.
Warm-season grasses, such as Bermuda grass, are commonly used for their high yield, good nutritional value, durability, and responsiveness to nitrogen fertilization. Alternatives include old world bluestem and crabgrass.
Alfalfa, a warm-season perennial legume, is widely used as hay in Oklahoma and can be grazed, though grazing may not always be economical.
Cool-season grasses such as wheat, rye, oats, barley, and ryegrass can be sod-seeded into dormant warm-season pastures to extend the grazing season. Combining ryegrass with small grains often allows grazing later into the spring. Cool-season clovers like red, white, and rose clover also thrive in Oklahoma and provide excellent nutrition.
However, it’s important to recognize and remove potentially toxic plants from horse pastures. These include bitterweed, black locust, cocklebur, horsetail, milkweed, ornamental yew, pigweed, snakeroot, St. John’s wort, wild parsley or carrot, and yarrow. Grasses in the Sorghum genus can contain prussic acid, which may cause severe health issues and even death. Clovers and small grains in humid conditions may also develop mold, which can be dangerous to horses.
Equine
No Foot, No Horse
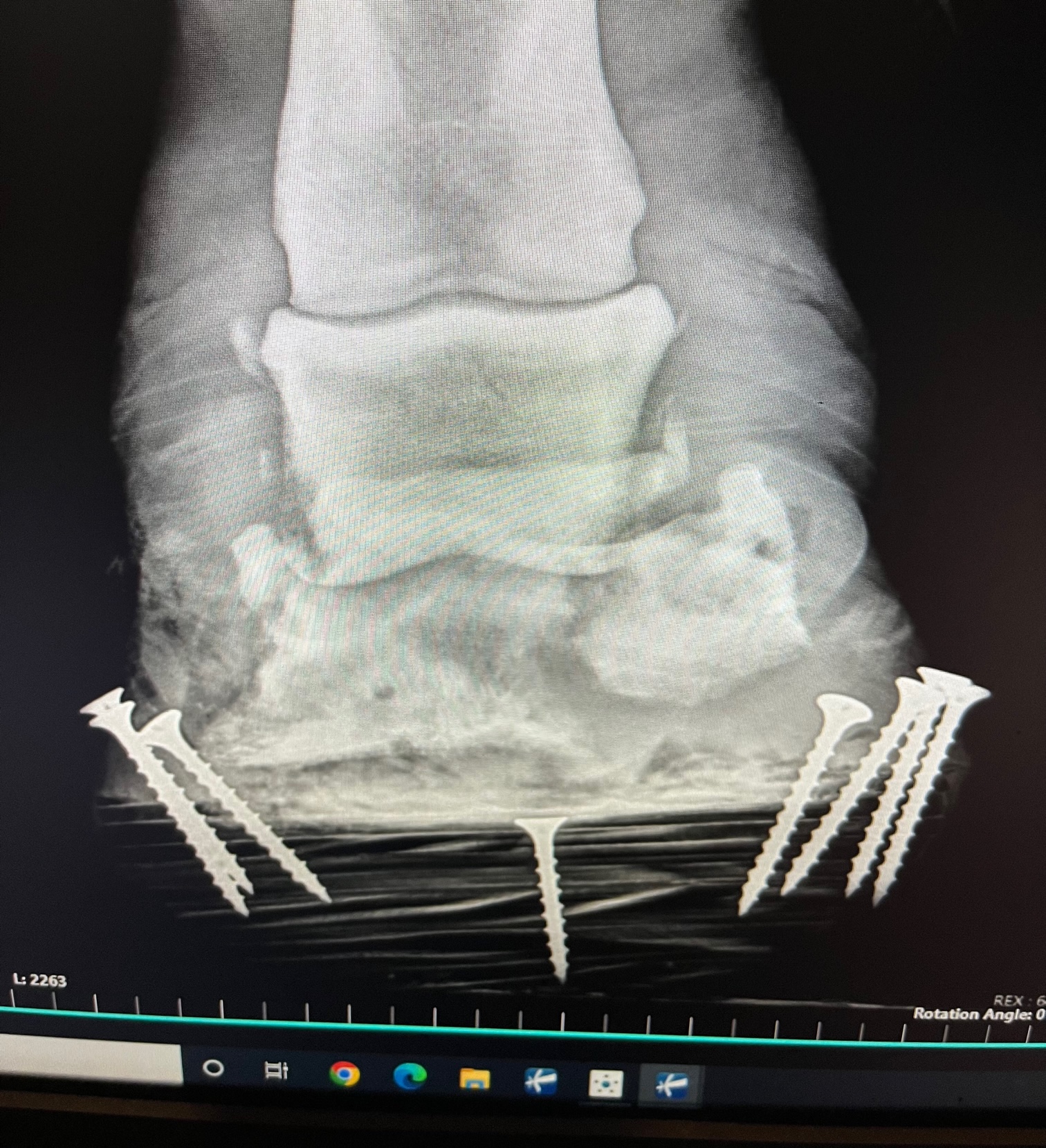
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf, DVM
There is a wise old saying no foot no horse and that is absolutely true. Horses of all breed, discipline and size must have good healthy feet or they will suffer poor performance, chronic pain or worse succumb to diseases of the foot. There are several medical conditions that require surgical treatment within the hoof wall of the horse and this article will highlight the most common conditions that require surgical treatment and specialty farrier care.
Foot Abscesses –
Foot abscesses are a very common issue that nearly every horse may experience at some point in their lifetime. Abscesses are often minor issues that can be easily corrected by a farrier or veterinarian getting access to the abscess to allow drainage but they can be rather debilitating and sometimes rather serious. Abscesses in general are localized pockets of infection that found its way into the sole or white line of the foot. These abscesses often form because there is some structural abnormality of the foot, trauma that led to bleeding under the sole or improper hoof care that has led to abnormal forces being applied to the foot and of course the old hot nail. For example trimming of the foot without relieving enough sole pressure can lead to overloading the sole and in turn sole bruising setting up for an abscess. Other common abnormalities of the foot that leads to abscessation are laminitis and club feet. These two conditions can cause tearing and stretching of the white line and allow bacteria plus moisture to enter deeper into the foot which in some cases can further destabilize an already unhealthy foot, leading to a life threatening situation. Deep abscess that go untreated for days or weeks can continue to invade and dissect through tissue planes leading to larger abscesses. These large abscess sometimes require surgical intervention to keep them from spreading and to eliminate the abscess all together.
Pedal Bone Osteitis
Pedal bone or the coffin bone is a very unique bone compared to others in the horse. The coffin bone is a rather porous bone that has intimate attachment to the foot capsule and sole. The bone and the hoof tissue has a very high amount of blood supply rightly so because of the vast amount of metabolic rate energy it uses to keep the foot supplied with nutrients. Whenever the hoof is diseased or compromised from laminitis or infection the blood supply can be compromised as well spelling disaster. The disaster that can ensue from these conditions is an infected portion of the coffin bone or sequestration of bone. Bone sequestrums are when bone lacks blood supply and is also infected by bacteria that thrive off of dead tissue. Bone sequestrums are generally rather treatable conditions because once removed the bone can heal but the coffin bone is not the same as other bones in the horse. The coffin bone lacks an outer soft tissue coating called periosteum. Periosteum is a very robust membrane outside of almost all bones that provide blood supply and support healing with progenitor cells and stem cells. The uniqueness of the coffin bone without this important layer leads to poor healing, a more delicate blood supply and makes is more prone to infectious insults.
Treatment of an infected piece of the coffin bone requires aggressive steps in order to prevent spread and destruction of the rest of the coffin bone. Further spread into the coffin bone can lead to further damage to the blood supply to the bone and hoof as well as weakening the bone to the point of fracture under the weight of the horse. Aggressive surgical debridement or removal of infected tissue and bone is the first required step to reduce the amount of infection present in the foot. Secondly is aggressive antibiotic therapy using local delivery methods and systemic routes of administration. Local antibiotic delivery is by means of antibiotic beads, pastes or ointments and by means of regional limb perfusions. Regional limb perfusions are 20-30 minute treatments where antibiotics are delivered to the affected limb via blood vessels in that limb. The antibiotic is held in the limb by a tourniquet above the application site to allow higher concentration of the drug to enter the target tissue or region of the limb. Lastly is proper support of the remaining hoof while still maintaining access to the infected areas to allow local treatment. This step cannot be overlooked and requires the work of a talented farrier to make it possible.
Quittor
Quittor is a chronic deep infection within one of the collateral cartilages of the coffin bone. The collateral cartilages are attached on both wings of the coffin bone and are often referred to on x-ray films as side bone. Lacerations, puncture wounds, trauma and abscesses of the foot can lead to infection of the collateral cartilage. To most people quittor doesn’t sound like a big deal and seems like it would be easily addressed with a few days of antibiotics but that is not the case. This infection deep in the foot can be like a smoldering fire that cannot be put out until the infected cartilage is removed. The diagnosis is usually straight forward because there is often a draining tract with swelling, heat and proud flesh centered over one of the collateral cartilages. The difficulty lies in finding and removing all of the infected tissue not to mention that you have to go through the hoof wall to get there. A hoof wall resection or a window cut in the side of the foot is often needed to access the infected tissue, allow drainage and local treatment at the same time. Quittor can be rather difficult and sometimes require multiple surgeries in order to get the infection cleared up. After the hoof wall resection is made often a specialized shoe will be needed to help protect and keep the foot stable until the hoof grows out the defect in the hoof wall.
Keratoma
Keratoma is a benign tumor like growth that arises from the hoof wall or laminar tissue of the foot called keratin. Keratin is what makes up our hair and nails. This growth continues to expand between the foot wall and the coffin bone leading to pressure necrosis and damage to the coffin bone. This abnormal keratin tissue is usually located at the toe region of the foot and is thought to be triggered by trauma to the hoof tissue. The most common signs of a keratoma are reoccurring foot abscesses in the same location and same foot, plus lameness that are localized to the foot. X-ray, CT and MRI can be used to diagnose keratoma formation within the foot. Often the keratoma is well formed enough to be seen with x-ray but sometimes advance imaging is necessary to make the diagnosis.
The only treatment and cure for a keratoma is surgical removal through the hoof wall. This requires a hoof wall resection with either an oscillating saw or drill bit to removal the hoof wall without damaging the coffin bone. A keratoma has an often distinct appearance by this off white crumbly type tissue that is often easily removed from the surrounding healthy hoof wall. After surgical removal a specialized shoe is needed to protect the foot and allow access to treatment of the surgical site to prevent infection.
Coffin Bone Fractures –
There are many different patterns or ways that a coffin bone can be fracture and some are more serious than others. To keep it simpler we break them down into articular or non-articular meaning do they enter the coffin joint or do they not. Non-articular coffin joint fractures generally are much less serious and can be healed without major surgery. Often times non-articular fractures are stabilized with a special shoe and casting tape placed around the foot to make the hoof itself the “splint” for the coffin bone nestled inside the hoof wall.
Articular fractures of the coffin bone are a much more serious problem because of the damage that is done to the coffin joint. A fracture into any joint is a serious threat to the health of the joint and requires surgical reconstruction as soon as possible to keep the joint from developing crippling arthritis. The trouble again with any surgery on the foot is that the bone is inside the foot making it difficult to access. There are techniques to place screws into the coffin bone through small hoof wall resections to allow stabilization of coffin bone fractures. It does require the right fracture pattern and location to make this surgical treatment a plausible option.
Street Nail
A street nail surgery is used to treatment of deep penetrating injuries that occur at the frog or sole that leads to infection of the bottom of the coffin bone, navicular bone and closely related surrounding soft tissue structures. Street nail procedures are often needed when a metal object such as a nail or screw penetrates and infects the one of the vital structures of the bottom of the foot. This window allows flushing of the synovial structures and removal of damaged/infected tissue. This procedure success is greatly improved with the use of an arthroscopic camera placed in the navicular bursa or coffin joint depending on what area the puncture wound involves. The arthroscope allows better visualization and more thorough flushing of debris and infection out of these tight spaces. Again this surgery cannot be successful with the application of a special shoed called a hospital treatment plate shoe that allows access to the bottom of the foot while keeping the foot clean and protected.
As you can see there is a pretty clear pattern to these hoof conditions: infection and the need for specialized farrier care. In order to be successful in treating these conditions the veterinary surgeon and farrier must work hand in hand to provide the best care for the horse. Although performing surgery on the foot of a horse is challenging and sometimes limited, it is often possible to have successful outcomes with a variety of different conditions.
-

 Attractions8 years ago
Attractions8 years ago48 Hours in Atoka Remembered
-

 Country Lifestyle9 months ago
Country Lifestyle9 months agoJuly 2017 Profile: J.W. Hart
-

 Country Lifestyle9 years ago
Country Lifestyle9 years agoThe House a Treasure Built
-

 Country Lifestyle4 years ago
Country Lifestyle4 years agoThe Two Sides of Colten Jesse
-

 Outdoors7 years ago
Outdoors7 years agoGrazing Oklahoma: Honey Locust
-

 Equine8 years ago
Equine8 years agoUmbilical Hernia
-

 Outdoors5 years ago
Outdoors5 years agoPecan Production Information: Online Resources for Growers
-

 Farm & Ranch7 years ago
Farm & Ranch7 years agoHackberry (Celtis spp.)





