Equine
Degenerative Suspensory Ligament Desmitis of the Horse
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf
The suspensory ligament is a vital component of the limb of a horse to produce normal locomotion and support. The suspensory ligament is a common area of concern in performance horses of various disciplines and can be single handedly the cause of lameness or performance issues. This article is going to look at a specific degenerative disease of the suspensory ligament and what horses are at risk for this disease.
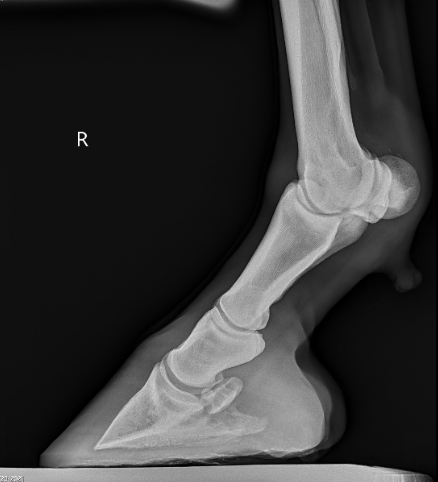
DSLD or degenerative suspensory ligament desmitis was first discovered in the early 1980’s in Peruvian Paso horses. The name has been changed because the suspensory ligament is not the only organ affected from the disease but the suspensory is ultimately the biggest issue. The newer name, ESPA or equine systemic proteoglycan accumulation, is more correct because other ligaments and tissues are affected by this disease. In this article we will only focus on the suspensory ligament. The most commonly affected breeds are Peruvian Paso, Paso Fino, Morgan, Saddlebred, Warmblood, Paints, American Quarter Horse, and Thoroughbred breeds. The age of onset of the disease is variable among breeds but it is more common to be seen in middle age to older horses. However it has been documented in horses as young as one year of age. The disease generally will have a slow insidious onset that can go undiagnosed for months or years depending on the horses work and discipline.
A horse that begins to show early signs of DSLD may have a vague lameness issue that is difficult to isolate and they most likely will resolve with a period of rest. As the horse returns to moderate level of work the lameness will return. This scenario may go on for several months or more before the discovery of the DSLD is made. The first indication of DSLD is often pain isolated in the suspensory branches or fetlock region when a flexion test is performed. Horses with DSLD will also have a “dropped” fetlock appearance because the suspensory is the main supporting structure of the fetlock joint. DSLD can affect the hind limbs, forelimbs or all limbs at the same time. A unique sign of DSLD is that not just one limb is affected but rather bilaterally affecting the limbs, meaning it will either affect either both forelimbs or hind limbs at the same time. It is my experience that the hind limbs are more commonly affected compared to the forelimbs. Horses will often have enlargement of the fetlock region and increased joint fluid or wind puffs. Horses will often have a straight hock or post legged hind limb appearance. Horses will often shift weight frequently in an effort to get relief from the discomfort and this can be confused with other lameness issues or foot related pain.
Diagnosis of DSLD is often made by clinical signs, breed and ultrasound findings. Ultrasound imaging of the suspensory ligaments will often show diffuse enlargement of the suspensory body and branches. The suspensory ligament will have a poor heterogeneous fiber pattern with periligamentious soft issue thickening from scar tissue deposition and edema or fluid within the tissue. Radiographs of the lower limb may reveal abnormal bone changes in the sesamoid bones behind the fetlock joints and even osteoarthritis of the pastern and or fetlock joints. A definitive diagnosis can be made from a biopsy of a ligament in the neck called the nuchal ligament, but is not often performed because of the invasiveness of the biopsy.
Treatment is very limited and it is mostly geared towards protection of further damage by prolonged rest. Pain management is also important to attempt to keep the horse as comfortable as possible. Different shoeing techniques can be used with marginal success. In early cases of DSLD, a suspensory shoe that helps engage more work from the deep digital flexor tendon can help elevate the fetlock and offer more protection to the suspensory ligament. The devastating thing about this disease is that there is no cure and there are hardly any good options to slow the progression of the disease. DSLD carries a poor prognosis when the diagnosis is made in any breed of horse or any discipline. Although some cases can be managed better than others, it often progresses to the point of debilitating pain and discomfort to the point of humane euthanasia especially in the Peruvian Paso breed.
Read more in the February 2023 issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
Equine
Horse Pasture ManagementBy OKFR Staff
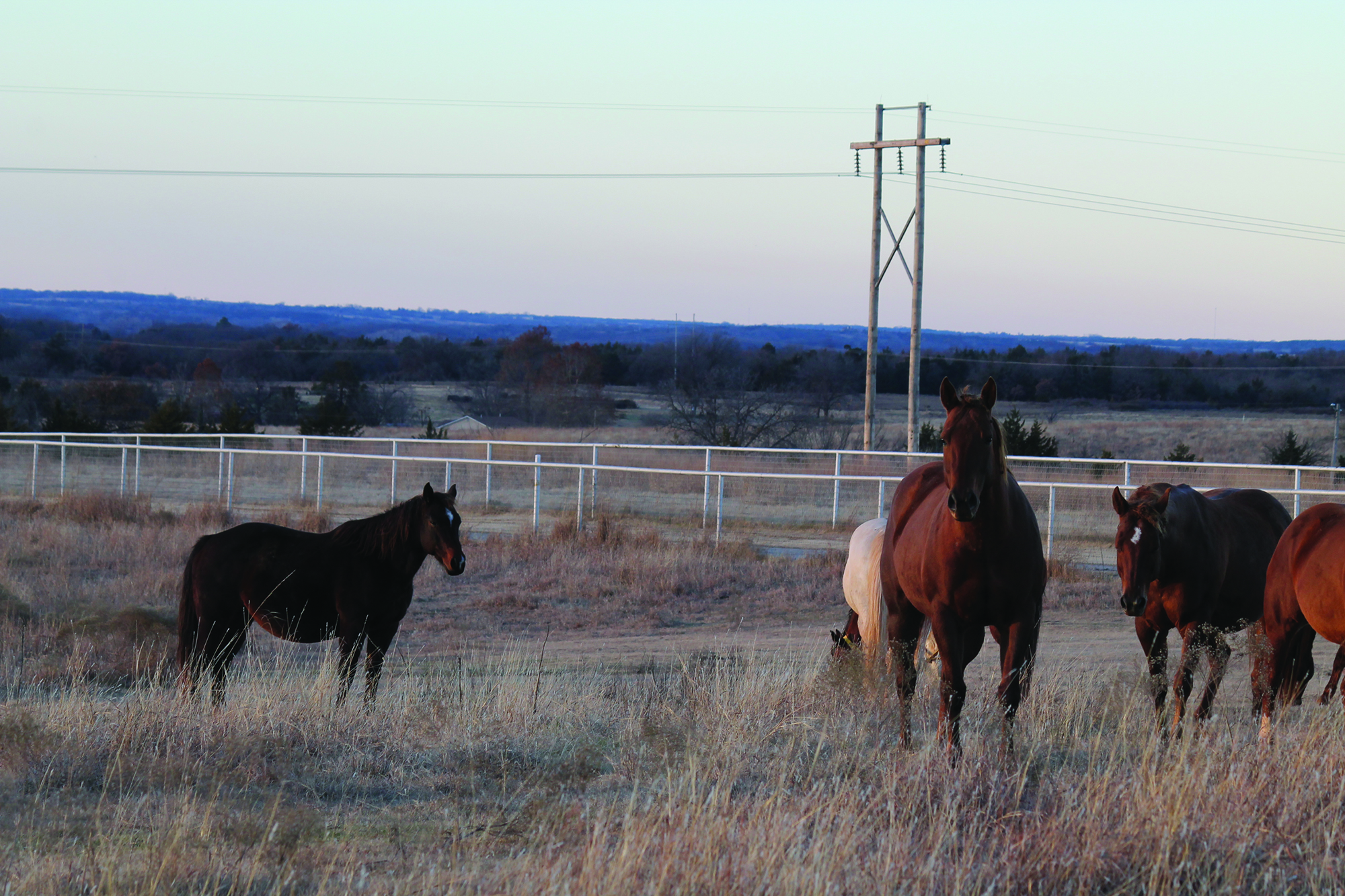

As spring weather arrives, horse owners are often eager to turn their horses out to graze and exercise—but is the pasture truly ready?
With proper management, pastures can serve as a high-quality forage source and a safe space for exercise. Effective management can even extend the forage production season, helping to reduce hay expenses. On the other hand, unmanaged pastures often develop weed problems, lack nutritional value, and can pose health risks for horses.
Here are five key steps to help improve and maintain horse pastures:
1. Soil Testing, Fertilizing, and Liming
Annual soil testing is ideal, but due to cost, testing every five years for grazing pastures and every three years for hay fields is a reasonable alternative. Grazing pastures tend to lose nutrients more slowly than hay fields because some nutrients are returned to the soil through horse waste, whereas nutrients in harvested hay are removed entirely.
For guidance on soil testing, fertilization, and liming, producers can refer to the Oklahoma Forage and Pasture Fertility Guide, available through Oklahoma Cooperative Extension and OSU’s Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources.
2. Over-Seeding and Renovating Bare Spots
Over-seeding helps replenish forage stands and prevent weed invasion. Use a high-quality pasture seed mix, limiting legume content to no more than 25 percent to avoid excessive salivation in horses.
3. Sacrifice Area
Creating a sacrifice area—a small, fenced section (approximately 300 square feet per horse)—gives overgrazed pastures time to recover during periods of heavy grazing or adverse weather. Horses kept in sacrifice areas should always have access to clean water, adequate hay, good drainage, and waste management.
4. Rotational Grazing
Horses are more selective grazers than cattle and will often overgraze their preferred plants, eventually killing them. This leads to spot grazing and pasture degradation. Rotational grazing allows plants time to regrow and helps reduce waste due to trampling.
Manure concentration in preferred areas also decreases grazing efficiency and nutrient distribution, making rotation an essential tool. Horses should be moved to a new pasture when forage is grazed down to 3–4 inches in height.
5. Weed Control
Chemical herbicides are commonly used to manage weeds, but identifying the specific weeds present is essential for selecting the right treatment. To prevent herbicide resistance, avoid long-term use of the same active ingredient and consider complementary methods such as mowing.
Maintaining healthy pasture also includes proper fertilization and rotational grazing, which both help minimize weed invasion.
Forage Selection and Toxic Plant Awareness
Selecting the right forage species depends on factors like land resources, management goals, and available capital. A mix of cool- and warm-season forages generally provides the most cost-effective year-round grazing.
Warm-season grasses, such as Bermuda grass, are commonly used for their high yield, good nutritional value, durability, and responsiveness to nitrogen fertilization. Alternatives include old world bluestem and crabgrass.
Alfalfa, a warm-season perennial legume, is widely used as hay in Oklahoma and can be grazed, though grazing may not always be economical.
Cool-season grasses such as wheat, rye, oats, barley, and ryegrass can be sod-seeded into dormant warm-season pastures to extend the grazing season. Combining ryegrass with small grains often allows grazing later into the spring. Cool-season clovers like red, white, and rose clover also thrive in Oklahoma and provide excellent nutrition.
However, it’s important to recognize and remove potentially toxic plants from horse pastures. These include bitterweed, black locust, cocklebur, horsetail, milkweed, ornamental yew, pigweed, snakeroot, St. John’s wort, wild parsley or carrot, and yarrow. Grasses in the Sorghum genus can contain prussic acid, which may cause severe health issues and even death. Clovers and small grains in humid conditions may also develop mold, which can be dangerous to horses.
Equine
No Foot, No Horse
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf, DVM
There is a wise old saying no foot no horse and that is absolutely true. Horses of all breed, discipline and size must have good healthy feet or they will suffer poor performance, chronic pain or worse succumb to diseases of the foot. There are several medical conditions that require surgical treatment within the hoof wall of the horse and this article will highlight the most common conditions that require surgical treatment and specialty farrier care.
Foot Abscesses –
Foot abscesses are a very common issue that nearly every horse may experience at some point in their lifetime. Abscesses are often minor issues that can be easily corrected by a farrier or veterinarian getting access to the abscess to allow drainage but they can be rather debilitating and sometimes rather serious. Abscesses in general are localized pockets of infection that found its way into the sole or white line of the foot. These abscesses often form because there is some structural abnormality of the foot, trauma that led to bleeding under the sole or improper hoof care that has led to abnormal forces being applied to the foot and of course the old hot nail. For example trimming of the foot without relieving enough sole pressure can lead to overloading the sole and in turn sole bruising setting up for an abscess. Other common abnormalities of the foot that leads to abscessation are laminitis and club feet. These two conditions can cause tearing and stretching of the white line and allow bacteria plus moisture to enter deeper into the foot which in some cases can further destabilize an already unhealthy foot, leading to a life threatening situation. Deep abscess that go untreated for days or weeks can continue to invade and dissect through tissue planes leading to larger abscesses. These large abscess sometimes require surgical intervention to keep them from spreading and to eliminate the abscess all together.
Pedal Bone Osteitis
Pedal bone or the coffin bone is a very unique bone compared to others in the horse. The coffin bone is a rather porous bone that has intimate attachment to the foot capsule and sole. The bone and the hoof tissue has a very high amount of blood supply rightly so because of the vast amount of metabolic rate energy it uses to keep the foot supplied with nutrients. Whenever the hoof is diseased or compromised from laminitis or infection the blood supply can be compromised as well spelling disaster. The disaster that can ensue from these conditions is an infected portion of the coffin bone or sequestration of bone. Bone sequestrums are when bone lacks blood supply and is also infected by bacteria that thrive off of dead tissue. Bone sequestrums are generally rather treatable conditions because once removed the bone can heal but the coffin bone is not the same as other bones in the horse. The coffin bone lacks an outer soft tissue coating called periosteum. Periosteum is a very robust membrane outside of almost all bones that provide blood supply and support healing with progenitor cells and stem cells. The uniqueness of the coffin bone without this important layer leads to poor healing, a more delicate blood supply and makes is more prone to infectious insults.
Treatment of an infected piece of the coffin bone requires aggressive steps in order to prevent spread and destruction of the rest of the coffin bone. Further spread into the coffin bone can lead to further damage to the blood supply to the bone and hoof as well as weakening the bone to the point of fracture under the weight of the horse. Aggressive surgical debridement or removal of infected tissue and bone is the first required step to reduce the amount of infection present in the foot. Secondly is aggressive antibiotic therapy using local delivery methods and systemic routes of administration. Local antibiotic delivery is by means of antibiotic beads, pastes or ointments and by means of regional limb perfusions. Regional limb perfusions are 20-30 minute treatments where antibiotics are delivered to the affected limb via blood vessels in that limb. The antibiotic is held in the limb by a tourniquet above the application site to allow higher concentration of the drug to enter the target tissue or region of the limb. Lastly is proper support of the remaining hoof while still maintaining access to the infected areas to allow local treatment. This step cannot be overlooked and requires the work of a talented farrier to make it possible.
Quittor
Quittor is a chronic deep infection within one of the collateral cartilages of the coffin bone. The collateral cartilages are attached on both wings of the coffin bone and are often referred to on x-ray films as side bone. Lacerations, puncture wounds, trauma and abscesses of the foot can lead to infection of the collateral cartilage. To most people quittor doesn’t sound like a big deal and seems like it would be easily addressed with a few days of antibiotics but that is not the case. This infection deep in the foot can be like a smoldering fire that cannot be put out until the infected cartilage is removed. The diagnosis is usually straight forward because there is often a draining tract with swelling, heat and proud flesh centered over one of the collateral cartilages. The difficulty lies in finding and removing all of the infected tissue not to mention that you have to go through the hoof wall to get there. A hoof wall resection or a window cut in the side of the foot is often needed to access the infected tissue, allow drainage and local treatment at the same time. Quittor can be rather difficult and sometimes require multiple surgeries in order to get the infection cleared up. After the hoof wall resection is made often a specialized shoe will be needed to help protect and keep the foot stable until the hoof grows out the defect in the hoof wall.
Keratoma
Keratoma is a benign tumor like growth that arises from the hoof wall or laminar tissue of the foot called keratin. Keratin is what makes up our hair and nails. This growth continues to expand between the foot wall and the coffin bone leading to pressure necrosis and damage to the coffin bone. This abnormal keratin tissue is usually located at the toe region of the foot and is thought to be triggered by trauma to the hoof tissue. The most common signs of a keratoma are reoccurring foot abscesses in the same location and same foot, plus lameness that are localized to the foot. X-ray, CT and MRI can be used to diagnose keratoma formation within the foot. Often the keratoma is well formed enough to be seen with x-ray but sometimes advance imaging is necessary to make the diagnosis.
The only treatment and cure for a keratoma is surgical removal through the hoof wall. This requires a hoof wall resection with either an oscillating saw or drill bit to removal the hoof wall without damaging the coffin bone. A keratoma has an often distinct appearance by this off white crumbly type tissue that is often easily removed from the surrounding healthy hoof wall. After surgical removal a specialized shoe is needed to protect the foot and allow access to treatment of the surgical site to prevent infection.
Coffin Bone Fractures –
There are many different patterns or ways that a coffin bone can be fracture and some are more serious than others. To keep it simpler we break them down into articular or non-articular meaning do they enter the coffin joint or do they not. Non-articular coffin joint fractures generally are much less serious and can be healed without major surgery. Often times non-articular fractures are stabilized with a special shoe and casting tape placed around the foot to make the hoof itself the “splint” for the coffin bone nestled inside the hoof wall.
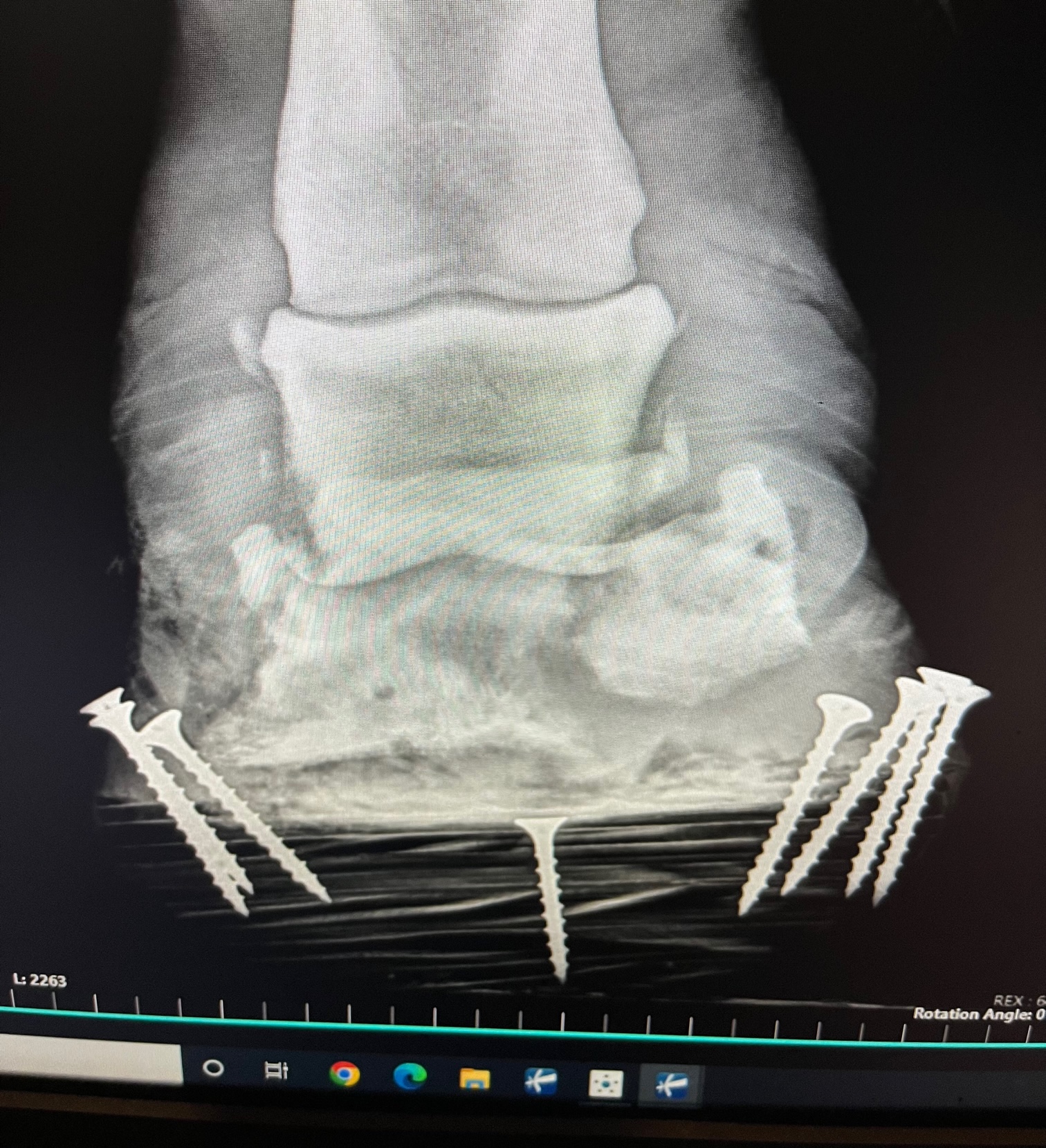
Articular fractures of the coffin bone are a much more serious problem because of the damage that is done to the coffin joint. A fracture into any joint is a serious threat to the health of the joint and requires surgical reconstruction as soon as possible to keep the joint from developing crippling arthritis. The trouble again with any surgery on the foot is that the bone is inside the foot making it difficult to access. There are techniques to place screws into the coffin bone through small hoof wall resections to allow stabilization of coffin bone fractures. It does require the right fracture pattern and location to make this surgical treatment a plausible option.
Street Nail
A street nail surgery is used to treatment of deep penetrating injuries that occur at the frog or sole that leads to infection of the bottom of the coffin bone, navicular bone and closely related surrounding soft tissue structures. Street nail procedures are often needed when a metal object such as a nail or screw penetrates and infects the one of the vital structures of the bottom of the foot. This window allows flushing of the synovial structures and removal of damaged/infected tissue. This procedure success is greatly improved with the use of an arthroscopic camera placed in the navicular bursa or coffin joint depending on what area the puncture wound involves. The arthroscope allows better visualization and more thorough flushing of debris and infection out of these tight spaces. Again this surgery cannot be successful with the application of a special shoed called a hospital treatment plate shoe that allows access to the bottom of the foot while keeping the foot clean and protected.
As you can see there is a pretty clear pattern to these hoof conditions: infection and the need for specialized farrier care. In order to be successful in treating these conditions the veterinary surgeon and farrier must work hand in hand to provide the best care for the horse. Although performing surgery on the foot of a horse is challenging and sometimes limited, it is often possible to have successful outcomes with a variety of different conditions.
Equine
Grain Overload in Horses
By Dr. Devon England
You come home after a long day at work, and your feed room door is wide open and grain bins are empty. What do you do? Before you call your vet, figure out what grains were eaten, try to estimate how much and determine which horse or horses got into the feed. Did your horse just get into some hay or alfalfa pellets, or did he get into a high sugar grain like Omolene 300? Did your horse get into chicken or cattle feed? If he did, is it a medicated feed, containing an ionophore like monensin or lasalocid?
Grain overload is an emergency, with better outcomes, the sooner the horse is treated. So, call your veterinarian as soon as you figure out a possible grain overload has occurred. Based on what feed and how much feed your horse consumed, your veterinarian can try to determine the risks to your horse and come up with a treatment plan. Signs of grain overload include colic, lethargy, inappetence, diarrhea and lameness. These signs will vary depending on how long ago grain ingestion occurred and the severity of grain overload.
If your horse got into hay or alfalfa pellets, these are low in sugar and therefore not a high risk for problems. Your horse may just have a mild belly ache (colic) episode. If your horse got into a feed like Omolene 300, they are at risk for grain overload. How severely they are affected will depend on a few factors including how much grain was eaten (5lb vs 30lb), if the horse normally receives that grain or doesn’t receive any grain, and the size of the horse vs the amount of grain eaten. Eating 5lb of grain for a full-size horse who normally receives grain may not be a problem, but that same amount of grain eaten by a small pony who normally only receives hay will be a problem.
Treatment for grain overload should be initiated as soon as possible. This includes lavaging the stomach to remove any remaining grain. Stomach lavage is only successful in removing feed within the first couple of hours. Horses will be given mineral oil or charcoal to decrease absorption of breakdown products (acids) from grain fermentation and protect the intestinal lining from damage. Intravenous fluids are given, because horses can quickly become dehydrated with grain overload, due to digestion products from the grain drawing in a lot of water into the colon. Anti-inflammatories, lidocaine, and ice boots are used in more severe cases to decrease the risk of laminitis. In more severe cases with damage of the intestinal lining, antibiotics may be used to prevent infections associated with bacterial escape from the damaged intestine.
If your horse got into medicated feed containing an ionophore, your horse is at high risk for heart failure and muscle damage, on top of grain overload. Ionophores are toxic at very low doses in horses (2mg/kg). These drugs are added to livestock feed to decrease parasites (coccidia), to help with feed efficiency, to decrease risk of bloat and to decrease methane emissions. If your horse has eaten ANY amount of medicated feed, they should be immediately seen by your veterinarian, even if they are not showing any clinical signs. Horses can have no clinical signs or be mildly lethargic in cases where small amounts of medicated feed were eaten but still have evidence on blood work or muscle and heart damage. Clinical signs include initial inappetence or colic signs, weakness or neurologic signs in the hind end, muscle fasciculations (twitching), laying down more, and not being able to stand. There is no anti-dote to ionophore toxicity. Treatment may include mineral oil, IV fluids, anti-inflammatories and supportive care, depending on how soon toxicity is identified. In severe cases, horses can die or develop heart failure, necessitating euthanasia. In less severe cases, especially if identified and treated early, horses can recover fully.
Grain overload can come with serious complications if severe or medicated feeds are involved, especially if treatment is delayed. Secure your feed room as best as possible and keep medicated livestock feeds in a separate location to prevent cross-contamination. And if you have any concerns about your horse getting into feed, call your veterinarian as soon as possible.
This article was originally published in the February 2025 issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
-

 Attractions8 years ago
Attractions8 years ago48 Hours in Atoka Remembered
-

 Country Lifestyle9 months ago
Country Lifestyle9 months agoJuly 2017 Profile: J.W. Hart
-

 Country Lifestyle9 years ago
Country Lifestyle9 years agoThe House a Treasure Built
-

 Country Lifestyle4 years ago
Country Lifestyle4 years agoThe Two Sides of Colten Jesse
-

 Outdoors7 years ago
Outdoors7 years agoGrazing Oklahoma: Honey Locust
-

 Equine8 years ago
Equine8 years agoUmbilical Hernia
-

 Outdoors5 years ago
Outdoors5 years agoPecan Production Information: Online Resources for Growers
-

 Farm & Ranch7 years ago
Farm & Ranch7 years agoHackberry (Celtis spp.)





