Attractions
A Versatile Venue
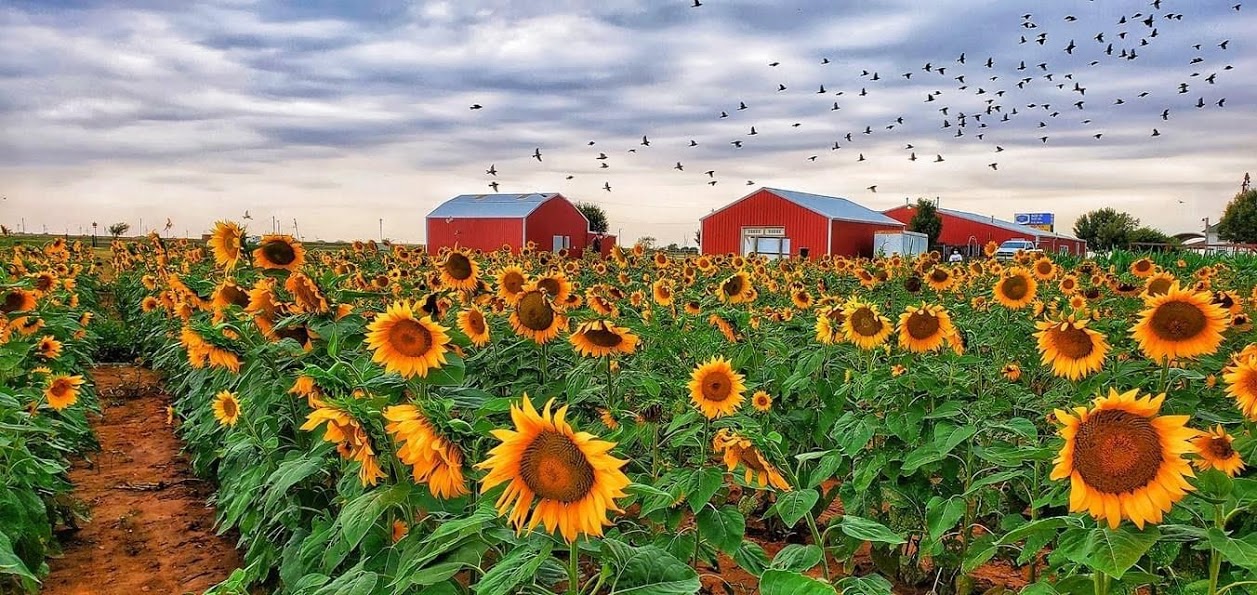

Fields that once were prolific with wheat have now found a new purpose at P Bar Farms in Hydro, Okla. Now, colorful sunflowers abound, attracting visitors from all across the state who come for photo opportunities. In another 10-acre section, specialty corn is grown specifically to be mowed to a specific pattern, transforming into a maze that sees upwards of 15,000[LM1] visitors annually.
It’s not that Loren and Kim Liebscher couldn’t make a traditional farm work; it’s more that they were looking for something fun to do for a few years.
P Bar Farms is named for Travis Payne, Kim’s father. “We used to farm traditionally here. We were farming and her dad got sick. I kind of lost my love to farm, so I began praying that God would give me something to put the fun back into farming,” Loren shared.
It was just two weeks later that God delivered a sign that would change the course for P Bar Farm. “I read in a Progressive Farmer magazine about a guy doing a corn maze in Nashville, Tenn. We found out that the first Annual Corn Maze Convention was only two or three weeks after that,” he said. “So, we drove to Salt Lake City for the first convention, and that’s how we got started.”
Loren and Kim admit they knew nothing about corn mazes, but they learned plenty during the convention. “The Convention was actually part of a franchise company that was looking to add farms. We joined, and for the fee they gave us all the secrets and designs for the maze and everything,” Loren explained.
After a few years, the Liebschers opted out of the franchise. “We felt like we knew what we were doing by then,” Kim said.
The first P Bar Farms corn maze was grown and cut in 2001, but then 9/11 happened. The uncertainty that plagued the country made its way to Hydro, and it wasn’t a given that the corn maze adventure would even get out of the gate. “We thought that was going to be the end. We had hoped that if we got 1,000 people to come during that first season, at $5 a person, we’d be doing well. A $5,000 addition to your income is pretty good for a farmer,” Loren said. “That first year we wound up having close to 5,000, even with 9/11. We had one customer explain it to us. She said, ‘I’ve never felt so safe having my kids so lost, but it’s a family farming operation, and nothing’s going to happen here on the farm. It has that good feeling where people feel safe and comfortable.”
Kim added, “We just wanted to have something fun that was light-hearted. We didn’t anticipate being busy – we were just having fun. We thought we could do it, but if not, we don’t have anything to lose.”
With the success of the first year, the Liebschers knew they would do the corn maze again. They built a barn and added a new concession stand. They also interviewed some tough critics; teachers that came out to the farm. “We had a retired schoolteacher that worked for us, and she said if you want to get the truth to interview teachers. So, we created a survey that all the teachers filled out, and everything that came back said it was wonderful, a great concept, and a great idea,” Loren said. “But, they added they weren’t coming back until we got indoor bathrooms. That was the number one request from the teachers, so we definitely made that change.”
As the interest in the corn maze grew, P Bar Farms continued to expand. First a petting zoo was added, and then a new barn. With more requests for parties, more buildings went up. The Liebschers wanted the property to resemble an old family farm, so they purchased an old home in Hinton, Okla., and moved it in. “We wanted to use it as a bed and breakfast. That never really worked out, but we rented it for a while. Now it’s regularly booked as an Airbnb. People like to get away and get out in the country,” Kim shared.
There have been very few noticeable failures in the past two decades. The only other memorable one was a venture with a greenhouse. “With the wind in Oklahoma, that didn’t work for us. We had put asphalt in the bottom of our greenhouse, so we used that and put in a new party barn,” Loren said.
Soon a pumpkin patch was added to compliment the maze and the rest of the farm. “We’ve always had a pumpkin patch. The problem is pumpkins can be really hard to grow if you don’t rotate them, so we don’t do that real well. Our first year we had more than we could sell, but after that we really were going through them. Now we’re going through 15-20,000 pumpkins a year, and we can’t grow that many, so we just buy them,” Loren added.
It was only a few years ago that the Liebschers added a sunflower patch to the mix, taking up a few more acres covered by the pivot. “The first year they were fun and pretty, but we didn’t have a lot of visitors. This year has been different, and I think our daughter is probably the reason for that success. She has a marketing degree and it’s been unbelievable,” Kim said. “Oklahoma Tourism did a post about a ‘mystical sunflower patch.’ Now people are here all the time while they’re blooming to take photos.”
The sunflower patch is just a few acres, but the Liebschers feel it’s the perfect size. “We have found that the smaller the patch, the better people take care of it,” he said. “Plus, sunflowers are tricky. They either make it or they don’t, but this has been a very good year for them.
Read more in the October issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
Attractions
Inventions of Agriculture: The Cotton Gin
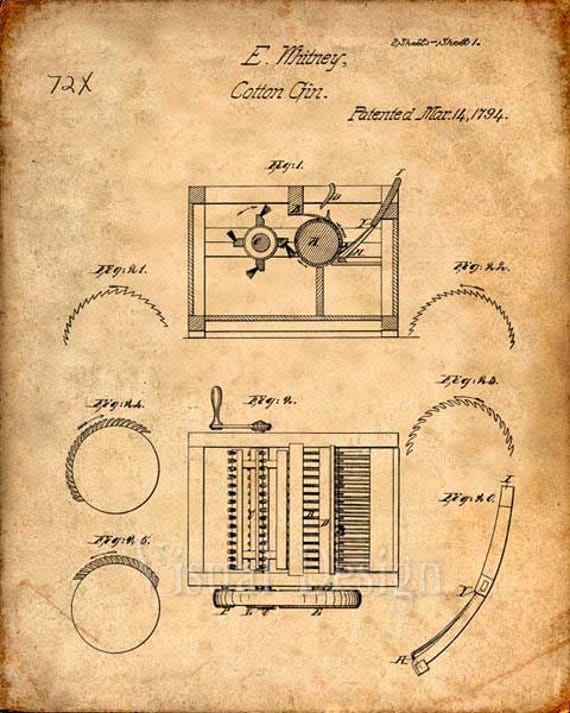
A few centuries ago, the landscape of farming and ranching looked quite different than it does today. There were no tractors for plowing, airplanes for spraying or even barbed wire for separating cattle.
There are inventions that have come along and changed the face of agriculture across the United States. One of those inventions was the cotton gin. It was invented during a time when the agricultural industry was struggling after its most significant crop, tobacco, saw revenues begin to plummet. But while it saved the profits and livelihood of many farmers and plantation owners, it also led to the increase in slave labor, making it an invention that significantly changed both our economic and social past.
The cotton gin was invented by Eli Whitney. Whitney was born in Westborough, Mass., on Dec. 8, 1765. His father was a farmer, and his son would prove his talents as both an inventor and a mechanic at a young age.
Whitney graduated Yale University and even considered becoming a lawyer, but life took him down a different path, one that would change the lives of farmers forever. He made his way to the south after graduation with plans to tutor, but upon arrival, he accepted a position with Catherine Green in Savannah, Ga. Greene was the widow of American Revolutionary War general Nathanael Greene and owned the Mulberry Grove plantation.
At the time, tobacco was falling in value due to both soil exhaustion and abundance. Farmers began turning to other crop options, including cotton. Unfortunately, the only variety that could be grown inland contained seeds that were time-consuming to pick out.
During the colonial times, cloth derived from cotton was more expensive than wool or even linen due to the difficulty of removing these seeds from the fibers. It took an entire day just to detach seeds from one single pound of cotton. Whitney’s employer, Greene, urged the young Whitney to find a solution to this problem. Her support was crucial in Whitney’s success in inventing the cotton gin. Some even suggest that it was actually Greene who was the true inventor of the cotton gin, but at the time, women were not allowed to apply for patents in the United States.
On March 14, 1794, Whitney succeeded in obtaining a patent for the cotton gin. While similar devices had been around for many years, his was the first single device that could clean short-staple cotton. The introduction of the new technology made cotton a profitable crop in the United States for the very first time.
The device worked much like a strainer. The cotton was run through a drum, made of wood, which included hooks similar to teeth along the perimeter. Those hooks caught the cotton fiber and drug them through a mesh, which was too small to allow the seeds through. However, the hooks pulled the cotton through easily.
Small cotton gins could easily be worked by hand, while larger ones included the use of horses to power. Even the smaller gin could remove seeds from 50 pounds of cotton in one day, a much larger amount than the results of doing it by hand. In fact, the gin allowed 1,000 pounds of cotton to be cleaned in the same amount of time it took a worker to do five pounds by hand.
Due to Whitney’s invention of the cotton gin, along with other inventions of the Industrial Revolution such as machines to weave it, the price of cotton plunged and production of it doubled each decade after 1800. It even began being shipped overseas, and soon American farmers were growing 75 percent of the world’s supply of cotton.
However, Whitney’s invention was not all good news. While it did increase the production and profits of crops in America, it also established the cotton plantation culture of the south. The cotton crop became so lucrative for plantation owners, the demand to make more significantly increased. As it did, so did the use of slave labor for growing it.
As for Whitney, he struggled with patent-law issues that prevented him from significantly profiting from his invention. He managed to overcome that obstacle when he secured a contract with the United State government in 1798 to create 10,000 muskets.
While it would take him a decade to make those instead of the two years originally planned in the contract, he began endorsing interchangeable parts. In other words, identical parts could be quickly assembled while making for easier repairs on machines. Many objects, from machines to guns, were constructed by individuals. While Whitney is most known for his invention of the cotton gin, he also is credited for the development of mass production within America.
In his personal life, Whitney did not wed until his 50s, when he married Henrietta Edwards in 1817. The pair would go on to have four children before his death on Jan. 8, 1825, at the age of 59.
Resources
History. (2010, February 4). Cotton Gin and Eli Whitney. A&E Television Networks. https://www.history.com/topics/inventions/cotton-gin-and-eli-whitney
National Archives and Records Administration. (2021, December 16). Eli Whitney’s Patent for the Cotton Gin. National Archives Educator Resources. https://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/cotton-gin-patent#background (Text adapted from an article written by Joan Brodsky Schur, a teacher at Village Community School in New York, N.Y.)
Attractions
Let’s Take A Trip – Part 1

After almost two years of Covid, testing, vaccinations, boosters, illness and death, wearing masks, staying indoors and away from others, severe thunderstorms, tornados, and now war in Europe, it’s time to get out and away from it all for at least a day.
Let’s get on I35 North of Ardmore and begin our trip in the Arbuckle Mountains. Stop at every scenic turnout to enjoy the awe-inspiring views of the trees, valleys, and rocks that according to archeologists formed during an earthquake eons ago.
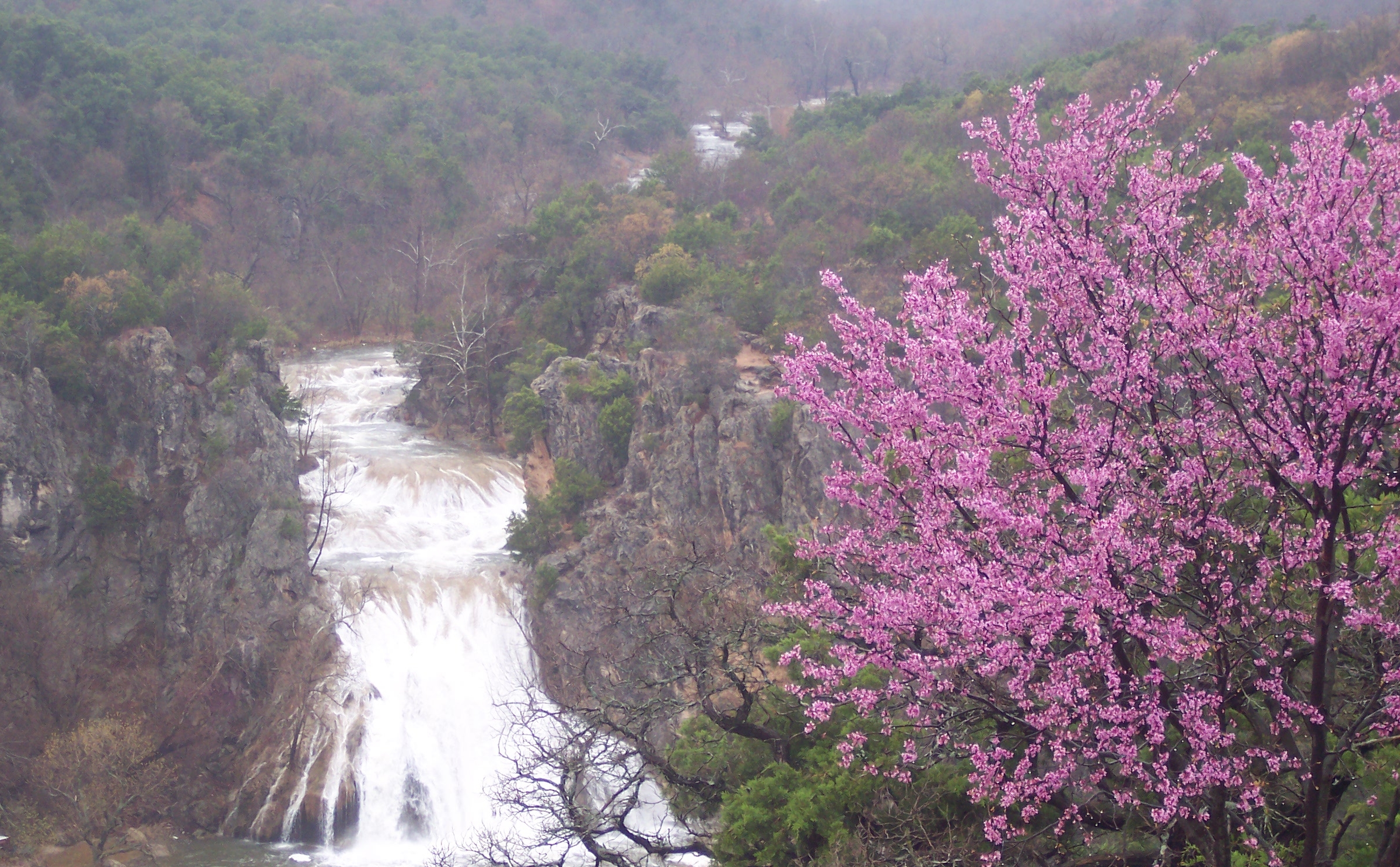
Reached by a narrow twisty highway, a sight comparable to a miniature Niagara Falls is soon revealed. Cascading 77 feet, Turner Falls is majestic. Formed by Honey Creek, it empties into a beautiful blue lake.
Although it may be tempting, climbing to the area behind the falls and sliding down the falls is prohibited by law because more than one person has drowned attempting lt.
Be sure to visit Collins Castle, built in the early 30`s of native materials as a summer home for Dr. Elizabeth Collins, a professor at Oklahoma University. It was once headquarters for the Bar C Ranch.
The entire park covers 1,500 acres and includes swimming areas, camping areas, cabins, hiking trails, caves, a water slide, trout fishing, and Look Out Point, featuring telescopes allowing you to view the entire park.
A zip line, diving, scubas, and floating on inner tubes entertains many visitors.
Children play areas, a trading post and majestic scenery attract more than 250,000 visitors each year.
Come for a day or a week and enjoy all the park has to offer.
Attractions
The Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society’s Oral History Collection

Listen not only to hear, but also to see and to act.
Listen to the words of the pioneers of Conservation and envision what they have seen and what they hoped for, and then practice it today and tomorrow on Oklahoma’s farms and ranches and within its growing urban areas.
That’s getting down to the subsoil or rather the essence of the Oklahoma Conservation Heritage Oral History Collection.
Just over two years ago the Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society announced the launch of this priceless conservation collection of passion, knowledge and effort.
The Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society partnered with the Oklahoma State University Library to record and archive interviews with individuals who have made contributions to conservation in Oklahoma. Audio, video, and transcripts of the interviews are posted digitally in the new Conservation Heritage Section of the OSU Library’s oral history collections. Interviews are available to researchers and the general public.
Oklahoma holds a unique place within the American conservation movement as the epicenter of the worst man-made ecological disaster in history, the Dustbowl. Out of the 1930s conservation districts were created by local farmers and ranchers who recognized the need to implement voluntary conservation practices on private working lands. Over the course of the last 80-plus years, Oklahoma has been a leader in the adoption of practices that benefit the health of our soils and water while building resiliency on our farms and ranches.
The Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society was formed in partnership with the Oklahoma Association of Conservation Districts, the Oklahoma Conservation Commission, the Natural Resources Conservation Service, the Oklahoma Chapter of the Soil and Waters Conservation Society and the RC&D Association. The Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society believes these interviews will preserve the storied and proud history of conservation in Oklahoma. This collection is a celebration of individuals and programs that have contributed to making Oklahoma known across the country as a leader in conservation.
Let us give you a couple of examples – Creede Speake, Jr., and Hal Clark – out of the many outstanding interviews you’ll hear in this collection.
Speake, born in Ardmore, Okla., in 1924 and a long-serving board member of the Caddo Watershed Association and of the Arbuckle Conservation District in Oklahoma, recalls his youth and his early interest in learning to be a pilot. He discusses some of his experiences serving during WWII and the Korean War and explains choices he made regarding his career as a rancher. Speake also talks about his involvement with conservation issues in his region and in the state and in particular his role in obtaining easements for upstream flood control structures.
A ways into the interview, Speake discusses managing grasslands. He said, “Native grass in this country is the most valuable thing you can have. You don’t have much at all, just management. Keep the weeds off of it, don’t have to fertilize it, but the four major native grasses we have here, they’re good. You get better gain and everything off of it. I wish everything I had was native grass. We’ve got a lot of Bermuda and other kinds of grass we have to fertilize.”
Clark, a graduate of Texas Tech University with a degree in Animal Science and Range Management, recalls his youth in the Panhandle of Oklahoma and Texas, relocating a couple times due to his father’s work, and his earliest memory of the impact of a flood. He discusses his early awareness of the issue of erosion and explains some conservation practices he has used to combat it. He also shares some of his experiences as a longtime member of the Cimarron County Conservation District (Oklahoma’s farthest western county) and his time as a member of the Oklahoma Conservation Commission.
Clark said, “We have a drier climate in Cimarron County, so it affects us in a lot of ways. The conservation challenges we have—Jimmy Emmons at (Dewey) County can grow a rotational crop that we can’t at Cimarron County because we don’t have the moisture. I wish we had rotation crops, something that could be plowed up (to improve the soil). I planted—on my farm, I planted Austrian winter peas a couple of times. Like that, it’s a legume. Cattle did pretty well on it, and I plowed it under to help the texture of the soil, because that’s the big issue now, people understanding what’s really underground—what’s in the soil that makes up what we’re trying to utilize to grow our crops or grass, so that’s a really important issue right now.”
Trey Lam has farmed on his family’s operation near Pauls Valley, Okla., for more than three decades and has served as the Executive Director of the Oklahoma Conservation Commission for more than five years. He has extensive knowledge of soil health, and he will quickly say that the bulk of it came from those two sources. He is quick to say that to lead in conservation you need to listen to soil health mentors and to the land itself.
“Please take the time to listen to these great Oklahomans tell their story of bringing our state back from an environmental disaster,” Lam said. “What a fantastic project teaching history in the first person. Conservationists want to leave the land better for the next generation. Now that generation can learn how these pioneers did it. We owe a huge thank you to the Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society.”
Sarah Blaney is Executive Director of the Oklahoma Association of Conservation Districts.
“Oklahoma’s conservation history is not just ours, but that of the entire nation,” Blaney said. “Many of the practices that have been adopted in soil and water conservation started right here in Oklahoma. It is wonderful that for generations to come, people will be able to learn from these conservationists. The Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society should be commended for doing an outstanding job preserving this important piece of rural, agriculture history.”
Ben Pollard is President of the Oklahoma Conservation Historical Society.
“We are most appreciative of the efforts of the Oral History Research Program at the OSU Library for working with us to create this collection,” Pollard said. “We have a proud conservation history in
To listen to the 23 completed oral histories, please visit: https://library.okstate.edu/oralhistory/digital/ or okconservation.org/history.
Read more in the July issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
-

 Country Lifestyle7 years ago
Country Lifestyle7 years agoJuly 2017 Profile: J.W. Hart
-

 Outdoors6 years ago
Outdoors6 years agoGrazing Oklahoma: Honey Locust
-

 Country Lifestyle2 years ago
Country Lifestyle2 years agoThe Two Sides of Colten Jesse
-

 Attractions7 years ago
Attractions7 years ago48 Hours in Atoka Remembered
-

 Farm & Ranch5 years ago
Farm & Ranch5 years agoHackberry (Celtis spp.)
-

 Outdoors4 years ago
Outdoors4 years agoPecan Production Information: Online Resources for Growers
-

 Equine7 years ago
Equine7 years agoUmbilical Hernia
-

 Country Lifestyle1 year ago
Country Lifestyle1 year agoSay Yes!




