Equine
No Foot, No Horse
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf, DVM
There is a wise old saying no foot no horse and that is absolutely true. Horses of all breed, discipline and size must have good healthy feet or they will suffer poor performance, chronic pain or worse succumb to diseases of the foot. There are several medical conditions that require surgical treatment within the hoof wall of the horse and this article will highlight the most common conditions that require surgical treatment and specialty farrier care.
Foot Abscesses –
Foot abscesses are a very common issue that nearly every horse may experience at some point in their lifetime. Abscesses are often minor issues that can be easily corrected by a farrier or veterinarian getting access to the abscess to allow drainage but they can be rather debilitating and sometimes rather serious. Abscesses in general are localized pockets of infection that found its way into the sole or white line of the foot. These abscesses often form because there is some structural abnormality of the foot, trauma that led to bleeding under the sole or improper hoof care that has led to abnormal forces being applied to the foot and of course the old hot nail. For example trimming of the foot without relieving enough sole pressure can lead to overloading the sole and in turn sole bruising setting up for an abscess. Other common abnormalities of the foot that leads to abscessation are laminitis and club feet. These two conditions can cause tearing and stretching of the white line and allow bacteria plus moisture to enter deeper into the foot which in some cases can further destabilize an already unhealthy foot, leading to a life threatening situation. Deep abscess that go untreated for days or weeks can continue to invade and dissect through tissue planes leading to larger abscesses. These large abscess sometimes require surgical intervention to keep them from spreading and to eliminate the abscess all together.
Pedal Bone Osteitis
Pedal bone or the coffin bone is a very unique bone compared to others in the horse. The coffin bone is a rather porous bone that has intimate attachment to the foot capsule and sole. The bone and the hoof tissue has a very high amount of blood supply rightly so because of the vast amount of metabolic rate energy it uses to keep the foot supplied with nutrients. Whenever the hoof is diseased or compromised from laminitis or infection the blood supply can be compromised as well spelling disaster. The disaster that can ensue from these conditions is an infected portion of the coffin bone or sequestration of bone. Bone sequestrums are when bone lacks blood supply and is also infected by bacteria that thrive off of dead tissue. Bone sequestrums are generally rather treatable conditions because once removed the bone can heal but the coffin bone is not the same as other bones in the horse. The coffin bone lacks an outer soft tissue coating called periosteum. Periosteum is a very robust membrane outside of almost all bones that provide blood supply and support healing with progenitor cells and stem cells. The uniqueness of the coffin bone without this important layer leads to poor healing, a more delicate blood supply and makes is more prone to infectious insults.
Treatment of an infected piece of the coffin bone requires aggressive steps in order to prevent spread and destruction of the rest of the coffin bone. Further spread into the coffin bone can lead to further damage to the blood supply to the bone and hoof as well as weakening the bone to the point of fracture under the weight of the horse. Aggressive surgical debridement or removal of infected tissue and bone is the first required step to reduce the amount of infection present in the foot. Secondly is aggressive antibiotic therapy using local delivery methods and systemic routes of administration. Local antibiotic delivery is by means of antibiotic beads, pastes or ointments and by means of regional limb perfusions. Regional limb perfusions are 20-30 minute treatments where antibiotics are delivered to the affected limb via blood vessels in that limb. The antibiotic is held in the limb by a tourniquet above the application site to allow higher concentration of the drug to enter the target tissue or region of the limb. Lastly is proper support of the remaining hoof while still maintaining access to the infected areas to allow local treatment. This step cannot be overlooked and requires the work of a talented farrier to make it possible.
Quittor
Quittor is a chronic deep infection within one of the collateral cartilages of the coffin bone. The collateral cartilages are attached on both wings of the coffin bone and are often referred to on x-ray films as side bone. Lacerations, puncture wounds, trauma and abscesses of the foot can lead to infection of the collateral cartilage. To most people quittor doesn’t sound like a big deal and seems like it would be easily addressed with a few days of antibiotics but that is not the case. This infection deep in the foot can be like a smoldering fire that cannot be put out until the infected cartilage is removed. The diagnosis is usually straight forward because there is often a draining tract with swelling, heat and proud flesh centered over one of the collateral cartilages. The difficulty lies in finding and removing all of the infected tissue not to mention that you have to go through the hoof wall to get there. A hoof wall resection or a window cut in the side of the foot is often needed to access the infected tissue, allow drainage and local treatment at the same time. Quittor can be rather difficult and sometimes require multiple surgeries in order to get the infection cleared up. After the hoof wall resection is made often a specialized shoe will be needed to help protect and keep the foot stable until the hoof grows out the defect in the hoof wall.
Keratoma
Keratoma is a benign tumor like growth that arises from the hoof wall or laminar tissue of the foot called keratin. Keratin is what makes up our hair and nails. This growth continues to expand between the foot wall and the coffin bone leading to pressure necrosis and damage to the coffin bone. This abnormal keratin tissue is usually located at the toe region of the foot and is thought to be triggered by trauma to the hoof tissue. The most common signs of a keratoma are reoccurring foot abscesses in the same location and same foot, plus lameness that are localized to the foot. X-ray, CT and MRI can be used to diagnose keratoma formation within the foot. Often the keratoma is well formed enough to be seen with x-ray but sometimes advance imaging is necessary to make the diagnosis.
The only treatment and cure for a keratoma is surgical removal through the hoof wall. This requires a hoof wall resection with either an oscillating saw or drill bit to removal the hoof wall without damaging the coffin bone. A keratoma has an often distinct appearance by this off white crumbly type tissue that is often easily removed from the surrounding healthy hoof wall. After surgical removal a specialized shoe is needed to protect the foot and allow access to treatment of the surgical site to prevent infection.
Coffin Bone Fractures –
There are many different patterns or ways that a coffin bone can be fracture and some are more serious than others. To keep it simpler we break them down into articular or non-articular meaning do they enter the coffin joint or do they not. Non-articular coffin joint fractures generally are much less serious and can be healed without major surgery. Often times non-articular fractures are stabilized with a special shoe and casting tape placed around the foot to make the hoof itself the “splint” for the coffin bone nestled inside the hoof wall.
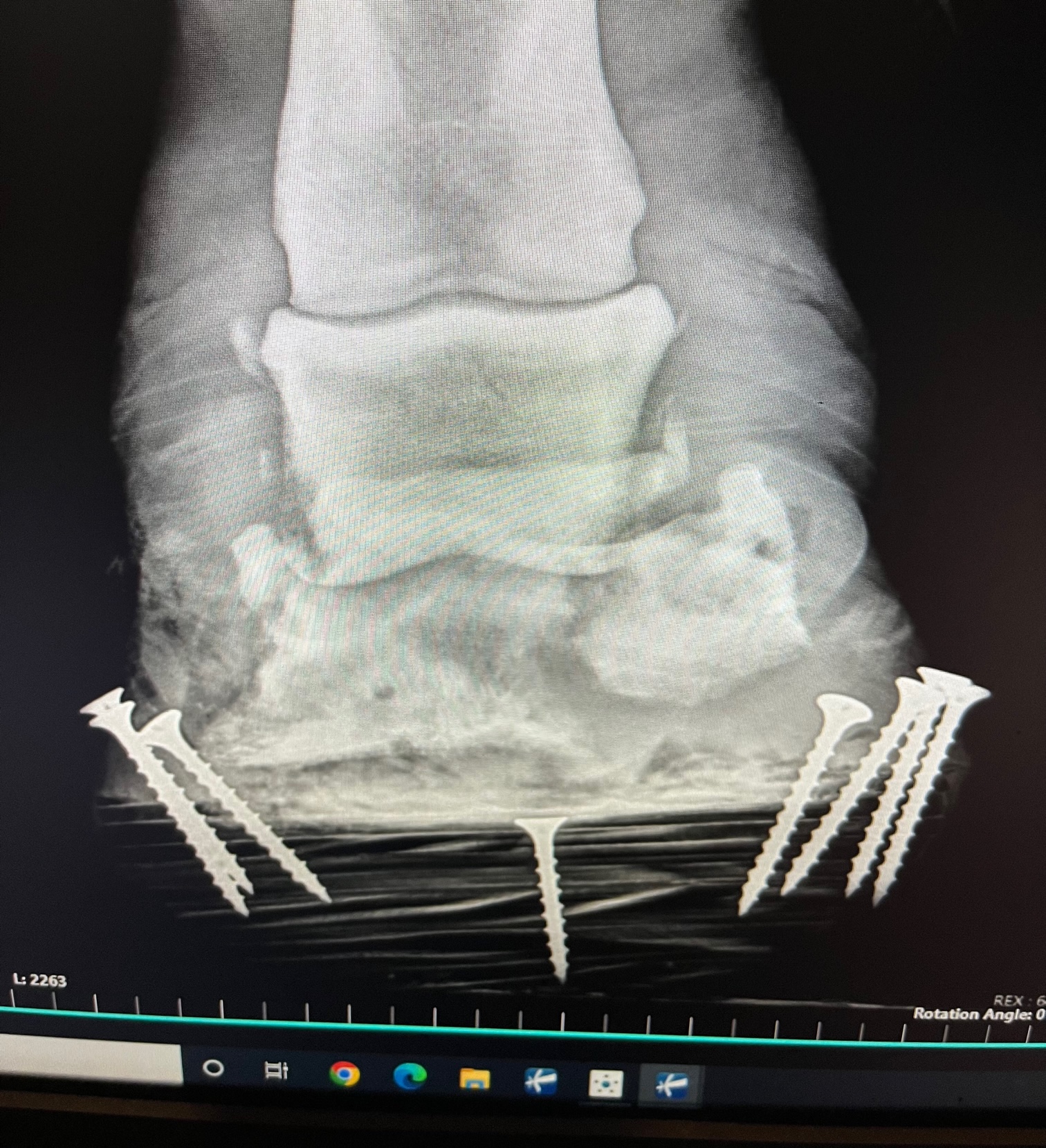
Articular fractures of the coffin bone are a much more serious problem because of the damage that is done to the coffin joint. A fracture into any joint is a serious threat to the health of the joint and requires surgical reconstruction as soon as possible to keep the joint from developing crippling arthritis. The trouble again with any surgery on the foot is that the bone is inside the foot making it difficult to access. There are techniques to place screws into the coffin bone through small hoof wall resections to allow stabilization of coffin bone fractures. It does require the right fracture pattern and location to make this surgical treatment a plausible option.
Street Nail
A street nail surgery is used to treatment of deep penetrating injuries that occur at the frog or sole that leads to infection of the bottom of the coffin bone, navicular bone and closely related surrounding soft tissue structures. Street nail procedures are often needed when a metal object such as a nail or screw penetrates and infects the one of the vital structures of the bottom of the foot. This window allows flushing of the synovial structures and removal of damaged/infected tissue. This procedure success is greatly improved with the use of an arthroscopic camera placed in the navicular bursa or coffin joint depending on what area the puncture wound involves. The arthroscope allows better visualization and more thorough flushing of debris and infection out of these tight spaces. Again this surgery cannot be successful with the application of a special shoed called a hospital treatment plate shoe that allows access to the bottom of the foot while keeping the foot clean and protected.
As you can see there is a pretty clear pattern to these hoof conditions: infection and the need for specialized farrier care. In order to be successful in treating these conditions the veterinary surgeon and farrier must work hand in hand to provide the best care for the horse. Although performing surgery on the foot of a horse is challenging and sometimes limited, it is often possible to have successful outcomes with a variety of different conditions.
Equine
Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) – The Easy Keeper Disease

By Garrett Metcalf
It is that time of year when cases in veterinary practices that are diagnosed with EMS or Equine Metabolic Syndrome spike. The reason cases of EMS spike are because the fast growth that pastures experience in the spring. Before EMS was well understood or discovered, many of these horses were diagnosed with grass founder, but through research the process of the disease is now better understood. The disease is caused by obese overfed horses and breeds of horses that have “hardy genes.” These are breeds that generally need less caloric intake to meet their daily energy needs. Although some breeds are at higher risk such as ponies, just about any breed can develop EMS.
Risk Factors for EMS
The key risk factor for development of EMS is weight gain, breed, high caloric intake and very little or inconsistent exercise. Horses that gain weight easily on pasture turn out or are getting too many calories from grains plus hay can be put at risk of EMS. Increasing levels of obesity in horses causes insulin resistance just like in humans, but fortunately for the horse, they have a very robust pancreas that is able to keep up with the extra demand for insulin to provide adequate amounts of glucose to tissue and organ systems despite the insulin resistance. This overproduction of insulin in order to keep up with the resistance causes a very key clinical sign of laminitis, which can be the most debilitating and difficult consequence of EMS. Over 90% of horses will present for laminitis as the first clinical sign of EMS. Unfortunately, the clinical signs for laminitis can go undetected for many months or even years in some cases until the progression of the laminitis reaches a very severe tipping point. It is not uncommon that horses with this disease go undetected for variable periods of time and have x-rays to prove it. Many times, horses will have rotation of the coffin bone in the hoof capsule upwards of 10 degrees before the horse is lame enough to alert their owners that there is a serious problem. It doesn’t seem possible that a horse can get that bad overnight, but rather in many cases they have mini laminitic episodes that are almost silent to many owners that lead to this much damage to their feet over time.
Identifying Horses at Risk
A common feature that puts horses at risk that owners can detect and address themselves before a laminitic crisis occurs is adipose deposited in certain areas of the horse’s body called regional adiposity. Regional adiposity describes fat or adipose tissue that is deposited in different regions of horses that owners should watch for if their horse is gaining weight. These common areas are the neck, commonly referred to as cresty necks, around the tail head, and sheaths of geldings or stallions. If these areas are noticed to be enlarging, especially in the spring when there is an abundance of fresh grass to graze on plus weight gain, then steps need to be taken to prevent the development of EMS.
Managing an Easy Keeper
It is very common to hear owners and veterinarians refer to heavy horses as easy keepers, but there can be some serious consequences of ignoring or brushing it off as just an easy keeper horse. Simple steps can be taken to reverse or reduce the risk of horses developing EMS by decreasing daily caloric intake. First, it is recommended to remove all grain from a horse’s diet including treats. Drastically reducing turn out time to graze especially fast growing lush grass is absolutely necessary in horses at risk of grass founder caused by EMS. There is some conflicting evidence as to when is the best time of day to allow a horse to graze that is sensitive to high sugars in lush growing grass. Some research has found that sugar levels peek later in the afternoon because of an abundance of sunshine and fully ramped up photosynthesis process that occurs in the grass. It is suggested then if grazing is allowed or deemed safe, that morning grazing is a safer time, but sometimes letting an at-risk horse graze is not worth the consequences. Other methods of allowing safe grazing are to mow the grass very short to minimize the volume of grass intake in a given period of time. If mowing is not an option, specially designed grazing muzzles allow pasture turn out but restrict the amount of grass taken in through the muzzle. Do not worry, as many horses are very quick to figure out how to get grass through the small hole in the muzzle and also allow the intake of water. It is recommended to have a leather poll strap on their halters to prevent injury when turned out while wearing a halter. Dry lot management is sometimes the only option, especially in horses that already have EMS. Keeping a horse on dry lot with no access to fresh grass and feeding more mature hay is sometimes needed to manage more severe cases. There are no current medications to help reduced the effects of insulin resistance due to obesity in horses, but some medications can be used to help with weight loss such as Thryo-L (levothyroxine) combined with consistent exercise.
Laminitis
Laminitis is the most debilitating and painful outcome of EMS, not to mention life threating. It is also the most expensive and difficult aspect of managing a horse with EMS. In order to properly manage laminitis caused by EMS, the horse needs to be examined by a veterinarian, radiographs need to be taken of the feet to assess the severity of the laminitis and an experienced farrier needs to be heavily involved with the management of the feet. If the disease is caught early, proper trimming may be all that is needed plus the other management aspects employed, of course, but in many cases corrective therapeutic shoeing is required. Pain management is another key aspect of addressing laminitis. NSAIDs or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, aspirin and an anticonvulsant drug called Gabapentin can help block or reduce pain of laminitis that horses experience. Some of these drugs do carry a risk of serious side effects so careful monitoring and proper dosages need to be on the order of a veterinarian to minimize the risk of side effects.
It cannot be repeated enough that the best cure for disease is through prevention. Taking early appropriate steps to keep horses from developing EMS is by far the best way to prevent the disease from occurring. If there is concern your horse is at risk of EMS, please talk to your veterinarian to determine if management and diet changes need to be made to prevent the development of this disease.
Equine
Cudd Quarter Horses Production & Consignment Sale Benefits Rein in Cancer

The Cudd Quarter Horses 38th annual sale is set for June 8 at the ranch in Woodward, Okla., and a special horse sold will benefit the Sooner State-based 501(c)(3) Rein in Cancer. Once again, Alice Goldseeker, a sorrel yearling mare by Bay John Goldseeker (King W Goldseeker x Jazzabell Jazz) out of Alices Cat (Cat Ichi x Squirrel Tooth Alice), will sell as lot #24 and, thanks to the generosity of Renee Jane Cudd, the proceed of her sale will go to benefit Rein in Cancer.
Rein in Cancer co-founder Shorty Koger expressed gratitude, saying, “We deeply appreciate Renee Cudd’s support of Rein in Cancer. The funds we provide are crucial for those facing the many challenges of cancer treatment.”
Cheryl Cody, President of Rein in Cancer, emphasized the importance of community support: “Support for Rein in Cancer means so much. The funds are allocated in two key ways: first, to sustain the Shirley Bowman Nutrition Center, which offers care to cancer patients regardless of their financial situation; and second, to provide direct financial assistance to individuals in the horse industry undergoing cancer treatment. Cancer affects everyone, whether personally or through loved ones, making this cause incredibly important. We are extremely grateful to Renee for her support.”
Cudd Quarter Horses was begun in 1985 by Renee Jane Cudd and her late husband, Bobby Joe Cudd. The ranch has been a leading breeder of AQHA Ranch and Roping horses for over 30 years, and the annual Production Sale is always a popular event. Renee noted, “Bobby Joe passed away in 2005, and I feel so lucky that I have been able to continue with it.”
For information on the sale, visit the Cudd Quarter Horses Facebook page.
Rein in Cancer was founded in 2007 by three friends: Shorty Koger of Shorty’s Caboy Hattery, Cheryl Cody of Pro Management, Inc., and healthcare professional Tracie Clark. These founders continue to lead the 501(c)(3) organization, which has raised millions of dollars. Rein in Cancer funds and supports the nutrition clinic at the University of Oklahoma’s Charles and Peggy Stephenson Cancer Center, offering services to all patients regardless of their ability to pay. Additionally, the organization provides direct financial assistance to individuals in the Western performance industry undergoing cancer treatments.
For information on Rein in Cancer, visit ReinInCancer.com.
Equine
Equine Flexural Limb Deformities
By Dr. Garrett Metcalf
Flexural limb issues can occur in different age groups of horses, starting with newborns up to two- to three-year-olds. These issues occur somewhat predictably in age groups and can be addressed rather quickly when needed. There are various treatments and methods that can be used to address flexural issues. This article will discuss the most common flexural abnormalities and treatment methods.
Foal Flexural Issues
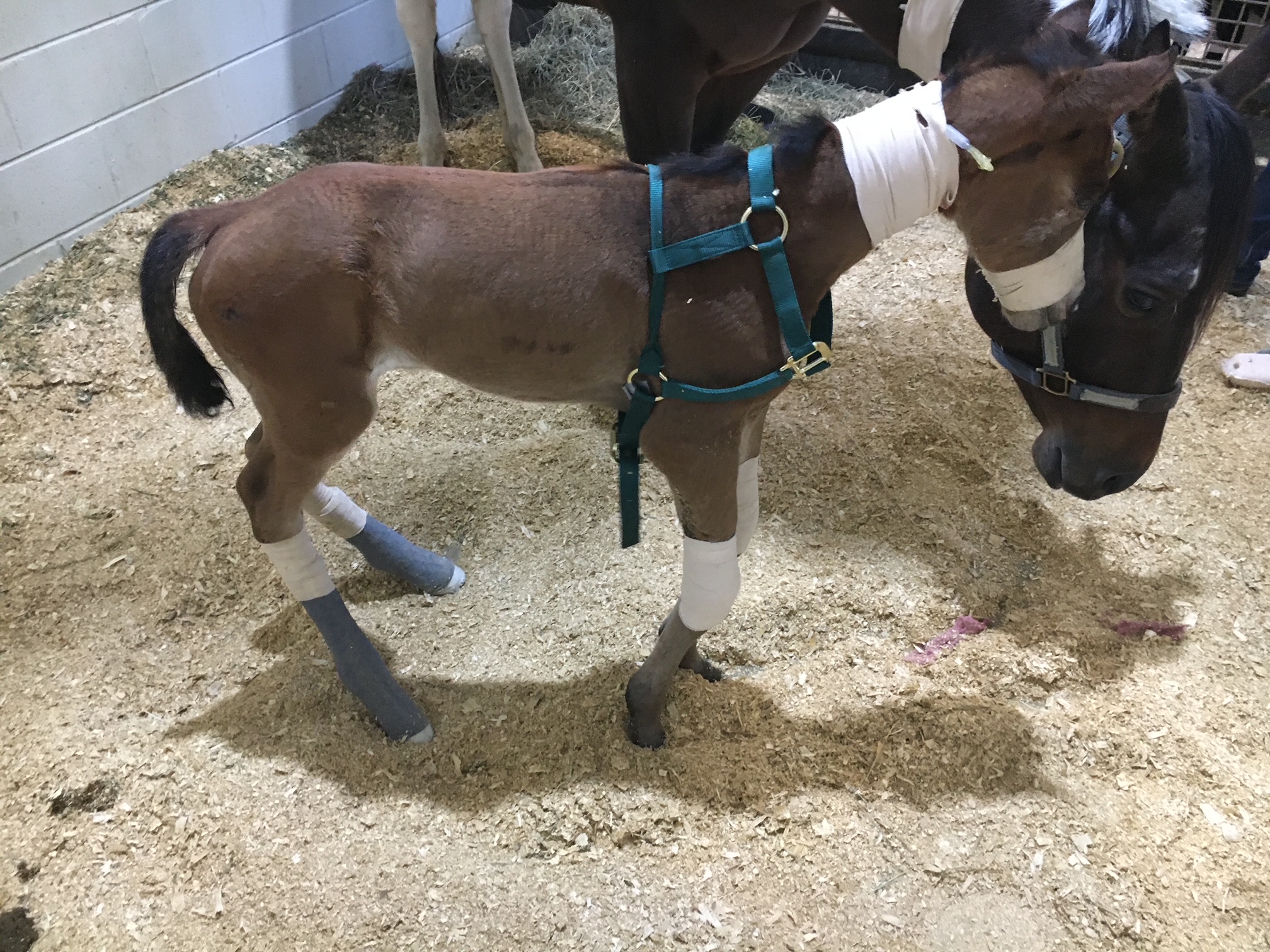
Foal flexural issues are often considered congenital flexural limb abnormalities because they are born with them. We don’t fully understand why this occurs but there is some evidence in the human literature that lack of fetal activity in the womb causes club feet in babies. In foals, it is thought that uterine positioning is to blame for part of the contracted tendons. Other causes can be exposure of the mare to toxic plants or substances that may be toxic to the fetus.
The most common area that a foal will have contracture of limb is at the carpus or knee. These foals will not be able to fully extend the knee and often will affect both at the same time. These foals can have difficulty standing to nurse or will get fatigued quickly and will not be able to stand for longer periods of time. There can also be damage to the extensor tendons or even rupture of extensor tendons caused by the high strain placed on them when the foal tries to stay standing. The rupturing of these tendons is not overly concerning but the lack of extensor function can make the flexural limb deformity worsen.
Other common locations of flexural limb deformities can be at the fetlock or coffin joint level. These deformities are not usually as detrimental to allowing the foal to stand and nurse properly compared to carpal flexural deformities. These deformities can be addressed similar to carpal deformities with some exceptions.
Treatment of Flexural Deformities
Splints or casts can be used to stretch and support the effected limbs of foals. Splints are often preferred by most veterinarians because they can be repositioned or reset as needed. Splints are easier to place on the limbs of foals but they do need resetting every 24 to 48 hours. Casting of the limbs is more rigid but is not adjustable once placed. Casting is often needed in more severe cases and requires changing frequently. Whenever placing these devices, care must be taken to prevent splint or cast sores because foal skin is rather delicate.
Surgical intervention is needed in some cases of carpal flexural deformities. A study out of Australia found that cutting of two muscle/tendon groups on the back of the carpus greatly improved the ability to extend the carpus with splinting methods. Cutting of these tendons do not have consequence to future athletic function. The two muscles are called flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnaris lateralis.
An antibiotic called Oxytetracycline is helpful to treat flexural limb deformities because of its side effect of causing tendon laxity. The laxity is created by chelating calcium within the tendons and allows the relaxation of tendons. This method does have some risk because of the high dose required and renal injury that it can cause when not administered with IV fluids.
Toe extension shoes are used when it comes to dealing with lower limb flexural limb deformities. These shoes are often applied with adhesives and after the splinting or casting is no longer needed. The toe extension shoe allow foal to continue to stretch those tendons every time they take a step and prevent from becoming contracted again.
Older horses (six months or older) with contracted tendons often get acquired limb deformities and the horses need surgical intervention to correct these deformities. These surgeries cut or release check ligaments that allows the musculotendinous unit of the deep digital or superficial digital flexor tendon to elongate. The deep digital flexor tendon is responsible for causing club feet or a flexural limb deformity at the coffin joint. The superficial digital flexor tendon is responsible flexor tendon that causes a flexural limb deformity at the fetlock joint. The check ligaments attach the tendon to bone and do not allow the tendon to elongate past a certain point. By eliminating these ligaments the flexural limb deformity can be corrected by allowing the muscle to stretch since the tendon is much more rigid.
Flexural limb deformities can be caused by excessive laxity or weakness of the tendons. These deformities are often seen in premature foals or foals that are born at a much smaller birth weight. The excessive laxity will cause the toes of there feet to flip up in the air and the fetlocks to be touching the ground. The areas where the skin is contacting the ground will cause sores and abrasions. If these areas are note protected the wounds can get into deep structures causing serious infection and injury the flexor tendons.
Treatment for tendon laxity is to add heel extension shoes to keep the toes flat to the ground. The extension behind the foot forces the toe down under the foals own weight. As the foal becomes stronger from normal activity the muscle attached to the tendons can support the foal and the limb laxity will correct itself. Abrasions still can occur even with heel extension shoes are in place so bandages need to be applied to protect these areas.
Flexural limb issues are a common issue that horses and owners will face. It is best to have your horse evaluated by a veterinarian whenever these problems are suspected. Foal flexural limb deformities can be life threatening because of the limitation of standing on time to nurse colostrum. Without colostrum within the first hours of life the foal is a much higher risk of sepsis and death.
Read more in the August 2023 issue of Oklahoma Farm & Ranch.
-

 Country Lifestyle7 years ago
Country Lifestyle7 years agoJuly 2017 Profile: J.W. Hart
-

 Outdoors6 years ago
Outdoors6 years agoGrazing Oklahoma: Honey Locust
-

 Country Lifestyle3 years ago
Country Lifestyle3 years agoThe Two Sides of Colten Jesse
-

 Outdoors4 years ago
Outdoors4 years agoPecan Production Information: Online Resources for Growers
-

 Equine7 years ago
Equine7 years agoUmbilical Hernia
-

 Attractions7 years ago
Attractions7 years ago48 Hours in Atoka Remembered
-

 Farm & Ranch6 years ago
Farm & Ranch6 years agoHackberry (Celtis spp.)
-

 Outdoors3 years ago
Outdoors3 years agoSuzy Landess: Conservation carries history into the future




